A web browser, such as Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox, is a computer program that enables users to browse and interact with websites online. It sends requests for web pages to servers hosting those pages and renders the received HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files into a visually appealing format for the user. The browser acts as a communication bridge between the user’s device and the vast network of servers hosting websites worldwide.
Upon receiving the requested files from the server, the browser interprets and renders them into an intuitive interface for viewing and interacting with the web content. This process involves translating HTML to structure content, CSS to style elements, and JavaScript to add interactive features. Through this mechanism, browsers empower users to traverse countless web pages effortlessly.
As technology advances, web browsers continually evolve to adapt to new standards and technologies while improving performance and security. They comprise several components working together seamlessly to provide a smooth browsing experience. In addition to displaying static text and images, modern browsers also support advanced functionalities such as multimedia playback, geolocation services, and offline storage capabilities.
In essence, web browsers play a pivotal role in enabling individuals worldwide to access diverse digital resources available on the internet easily. Their ongoing development ensures users can harness innovative web technologies while enjoying an intuitive tool for exploring online content across multiple devices.
Web browsers come in many options, yet they generally possess similar characteristics. One of the key features is the user interface, which plays a crucial role in rendering web pages for enhanced accessibility by users. The user interface is a communication bridge between the user and the browser, promoting better understanding and interaction.
Additionally, web browsers offer convenient features such as bookmarks and forward/back buttons to facilitate seamless navigation. These built-in tools aim to enhance users’ overall browsing experience and efficiency. Furthermore, modern web browsers often include customisable settings and extensions to tailor the browsing experience to individual preferences.
By prioritising a clean and intuitive user interface, web browsers strive to create an environment that encourages efficient utilisation and positive user interactions. It’s through these shared features that various browsers seek to deliver an optimal online experience.
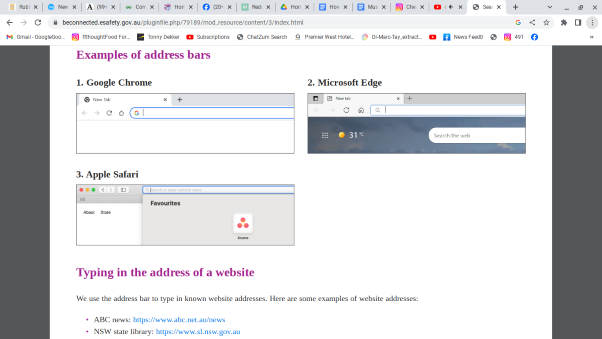
The address bar is a crucial element of a web browser, serving as a search and navigation tool for users. It allows individuals to enter URLs or search terms to access specific websites or conduct online searches. Additionally, the address bar displays the current web address of the site being accessed, providing users with constant visibility of their location within the online space.
When a user types in a URL or search query into the address bar and presses Enter, the browser uses this information to fetch the corresponding webpage from the internet. The address bar also supports auto-complete functionality, offering suggestions based on a user’s browsing history and bookmarks to expedite navigation.
Furthermore, many modern browsers integrate additional features into the address bar, such as displaying security indicators for secure websites (HTTPS) and allowing quick access to frequently visited sites. Overall, the address bar is essential in enabling seamless and efficient web browsing for users across various online platforms.
A rendering engine is a crucial component of web browsers, responsible for interpreting and displaying the content of web pages received from servers. Each browser utilises its unique rendering engine, resulting in variations in how web pages are rendered and displayed to users. For instance, Google Chrome employs the Blink rendering engine, Safari uses WebKit, and Firefox uses Gecko.
These engines play a crucial role in interpreting HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and other web technologies to present the final visual representation of a website. They handle tasks such as parsing HTML documents, executing JavaScript code, applying stylesheets to elements, and rendering multimedia content like images and videos. Because of the differing approaches taken by each rendering engine, websites may appear differently across various browsers.
Additionally, rendering engines are constantly developing to improve performance, speed, and compatibility with evolving web standards. Technical advancements in graphics processing and code optimization enhance the capabilities of modern rendering engines. As a result, smooth browsing experiences are made possible through the efficient interpretation and presentation of complex web content.
A rendering engine is a crucial component of web browsers, responsible for interpreting and displaying the content of web pages received from servers. Each browser utilises its unique rendering engine, resulting in variations in how web pages are rendered and displayed to users. For instance, Google Chrome employs the Blink rendering engine, Safari uses WebKit, and Firefox uses Gecko.
These engines play a crucial role in interpreting HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and other web technologies to present the final visual representation of a website. They handle tasks such as parsing HTML documents, executing JavaScript code, applying stylesheets to elements, and rendering multimedia content like images and videos. Because of the differing approaches taken by each rendering engine, websites may appear differently across various browsers.
Additionally, rendering engines are constantly developing to improve performance, speed, and compatibility with evolving web standards. Technical advancements in graphics processing and code optimisation enhance the capabilities of modern rendering engines. As a result, smooth browsing experiences are made possible through the efficient interpretation and presentation of complex web content.
Web browsers have a convenient feature called bookmarks that allows users to save frequently visited websites for easy access. When you bookmark a website, you no longer need to type the web address into the browser’s search bar whenever you want to visit it. Instead, you can click the bookmarked link and be directed to the site.
This feature saves time and effort when visiting favourite websites, online stores, or frequently accessed pages. Organising bookmarks into folders or categories allows users to keep their Internet browsing experience well-structured and efficient. Whether news websites, social media platforms, or educational resources, bookmarks provide quick access to desired content with just a single click.
Furthermore, modern web browsers offer syncing capabilities that allow users to access their bookmarks across different devices. This means that a website saved as a bookmark on one device can also be easily accessed from another device using the same web browser account.
Bookmarks are indispensable for streamlining web browsing and ensuring convenient access to preferred online destinations.
History is a built-in feature of web browsers that captures and stores a user’s online activity record. It keeps track of the websites visited and the specific pages within those sites that were accessed. This feature enables users to quickly retrace their browsing history, making it convenient to revisit previously viewed content.
To access the browsing history in most web browsers, users simply need to click an icon or button in the top right corner of the browser window. By doing so, a dropdown menu or new window will appear, displaying a list of recently visited websites and web pages. This functionality provides valuable insight into one’s online habits and can help find and revisit specific content.
In addition, the browsing history feature can be helpful for quickly locating a previously viewed webpage without needing to recall its exact URL or perform another search. Users also have the option to clear their browsing history, which can help protect privacy and free up space on their devices by removing potentially large amounts of stored data.
A download manager is a built-in feature of web browsers that allows users to keep track of and organise their downloads. It provides a convenient way for users to monitor the progress of their downloads, pause and resume them, and categorise them into different folders.
One key benefit of using a download manager is the ability to prioritise downloads based on user preferences. This can help optimise bandwidth use and ensure that important files are downloaded first.
Additionally, download managers often have features for scanning files for viruses or malware before they are saved to the user’s device, providing an extra layer of security. Some download managers also support batch downloading, allowing users to queue multiple files for simultaneous downloading.
Furthermore, many download managers offer scheduling options, enabling users to set specific download times to avoid peak internet usage hours or take advantage of off-peak times with faster speeds.
A download manager can enhance users’ experience by simplifying, managing and organising their downloads while providing added security and flexibility.
Customisation is an essential aspect of web browsers, allowing users to tailor their browsing experience to their preferences. This includes modifying the browser’s appearance, such as changing themes or adjusting the layout of toolbars and menus. Additionally, users can customise settings related to privacy, security, and accessibility to better suit their needs.
Furthermore, web browsers offer customisation options for managing downloads and viewing browsing history.
Users can choose where downloaded files are saved on their device and set preferences for how downloads are handled, such as prompting for a download location or automatically saving them to a specified folder. The history feature allows users to personalise how their browsing history is displayed and managed, including options for clearing specific entries or configuring how frequently history data is removed.
In essence, web browser customisation empowers users to mould their browsing environment according to their requirements and preferences, enhancing usability and personalisation.
Privacy and security features are essential components of a web browser, as they play a crucial role in safeguarding user data and ensuring safe online experiences. For instance, the incognito mode in Chrome allows for anonymous and secure browsing by not storing browsing history or cookies on the device. Additionally, ad and pop-up blockers help prevent intrusive advertisements and potential security threats from appearing during web sessions.
A password manager feature can also be included within the browser to securely store and manage user passwords, reducing the risk of unauthorised access to personal accounts. Moreover, a secure download manager ensures that downloaded files are scanned for malware and other potential threats before being saved on the device. These features collectively enhance privacy and security while using the web browser.
The Developer Tools is an essential feature that provides developers with additional benefits, allowing them to debug and analyse web pages more effectively. This tool offers tabs such as Element, Console, Sources, and Networks, each serving a different purpose. The Element tab allows developers to inspect and modify the HTML and CSS of a webpage, while the Console tab enables them to run JavaScript code and view error messages.
Furthermore, the Sources tab provides access to the source files of the webpage, facilitating debugging and making changes directly within the browser. The Network tab allows developers to monitor network activity, including requests and responses, which is vital for optimising website performance. These features are indispensable for developers seeking to understand and improve their web pages’ functionality and performance.
Cross-platform compatibility is a crucial attribute of a web browser, enabling it to function seamlessly across different operating systems. Users can access the same browser on various platforms, such as Windows, macOS, Linux, and iOS, without encountering compatibility issues. Whether surfing the web on a Windows desktop, a MacBook, or an iPhone, a cross-platform compatible browser ensures consistent performance and user experience.
This feature mainly benefits individuals who regularly switch between devices with different operating systems. It allows them to maintain their preferred browser across all devices without sacrificing functionality. Additionally, cross-platform compatibility contributes to a more unified browsing experience, as users can seamlessly synchronise bookmarks, history, and other settings across various platforms.
Maxthon browser is designed to provide users with many features to improve their browsing experience. One notable function is its ad-blocking capability, which helps prevent intrusive advertisements from disrupting users’ online activities. Moreover, the built-in screen capture tool allows users to capture and save screenshots within the browser conveniently.
In addition, Maxthon offers mouse gestures for efficient navigation, allowing users to perform various commands and actions with simple mouse movements. This feature can significantly streamline the browsing process and boost productivity. Furthermore, Maxthon provides a cloud backup and syncing service, enabling users to securely store and synchronise their bookmarks and browsing history across multiple devices.
This service allows users to access their personalised browsing data from different platforms without worrying about data loss or discrepancies. Overall, Maxthon’s diverse range of functions is tailored to cater to the needs of modern internet users, aiming to offer convenience, security, and efficiency in their online activities.
Maxthon browser offers a variety of functions to enhance the user experience. These functions include ad blocking, built-in screen capture, and mouse gestures for efficient navigation. Additionally, Maxthon features a cloud backup and syncing service to store bookmarks and browsing history across multiple devices.
The browser supports extensions and provides access to an extensive library of add-ons for customisation purposes. Furthermore, Maxthon offers a reader mode for distraction-free reading and a night mode for reduced eye strain during nighttime browsing. Users can also use built-in tools like note-taking and split-screen viewing to improve productivity while browsing the web.
With security in mind, Maxthon includes features such as secure site verification and anti-tracking protections to ensure user privacy. The browser’s speed optimisation delivers fast loading times and smooth performance for seamless web surfing. Overall, the functions in Maxthon provide users with a comprehensive suite of tools tailored to meet their browsing needs.
Moreover, this feature eliminates the need for users to search for alternative browsers specific to each operating system they use. Instead, they can rely on one browser that meets their requirements regardless of the platform they are using at any given time. Ultimately, cross-platform compatibility simplifies the user’s browsing experience by offering a consistent interface and feature set across multiple devices and operating systems.