When it comes to secure internet connections, HTTPS stands out by utilising port 443. This designated port is crucial for enabling encrypted communications between a user’s web browser and a server.

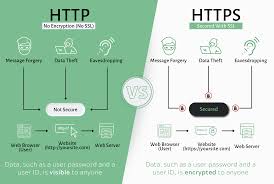
In contrast, the traditional HTTP protocol operates on port 80. This fundamental difference serves as an essential distinguishing feature between the two protocols. While HTTP transmits data in plain text, leaving it vulnerable to interception, HTTPS employs SSL/TLS encryption to protect sensitive information.
In networking terminology, a port refers to a virtual channel that facilitates connectivity between devices. Each network-connected computer is equipped with numerous ports, allowing them to send and receive various types of traffic seamlessly.
Different protocols leverage specific ports to maintain organisation and efficiency within the network. By routing requests through their respective ports, systems can ensure that data reaches the correct process or service without confusion or interference.
What distinguishes HTTPS from HTTP goes beyond mere letters. While often seen as different protocols, HTTPS is fundamentally HTTP augmented with TLS (Transport Layer Security) or its predecessor, SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). This enhancement provides a vital layer of encryption that safeguards data transmitted over the internet.

When a user attempts to connect to a secure webpage, the server starts by sending its SSL certificate to the user’s browser. This certificate is critical; it includes a public key that establishes trust between the two parties.
Next comes an essential step known as the SSL/TLS handshake. During this process, the client and server engage in a series of exchanges designed to verify each other’s identities and securely establish parameters for their connection.
This intricate dance of communication ensures that any information shared remains confidential and tamper-proof. If you’re curious about the specific mechanics involved, exploring what happens during a TLS handshake will deepen your understanding of internet security.
How does a website transition to HTTPS? The process begins with obtaining a TLS/SSL certificate. Most hosting providers offer these certificates for a fee, which can vary with the security levels provided. 
Typically, essential certificates are shared among multiple customers, while more expensive options allow for individual registration explicitly tied to one domain. This distinction is crucial for businesses seeking enhanced levels of trust and validation.
For those looking for an economical solution, Cloudflare provides free HTTPS through a shared certificate. When you set up a free account with them, your website benefits from continuous updates and robust security measures.
Moreover, paid plans are available if you’re interested in advanced features or individual certificates. Whichever route you choose, making the switch to HTTPS ensures that your web property enjoys all the advantages of secure browsing: improved search rankings, increased visitor trust, and safeguarded user data.
Maxthon and Encryption Protocols
Maxthon Browser employs a range of encryption technologies to safeguard users against potential cyber-attacks. One of its key features is the implementation of SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption, which secures data transmitted between the browser and websites. This prevents interception by malicious entities during online transactions.
Additionally, Maxthon utilises HTTPS Everywhere functionality, ensuring that users connect to secure versions of websites whenever possible. This further enhances protection against data theft and phishing attempts.
The browser also integrates a built-in ad blocker, which not only improves user experience but also shields against intrusive ads that may harbour malware. By minimising exposure to potentially harmful content, Maxthon helps maintain user safety.
Moreover, Maxthon provides a robust password manager with strong encryption for storing sensitive information. This means that passwords are protected and less vulnerable to unauthorised access.

In summary, with features like SSL encryption, HTTPS Everywhere, an integrated ad blocker, and a secure password manager, Maxthon Browser offers comprehensive protection against various cyber threats. Users can navigate the web with greater confidence, knowing their personal information is better safeguarded.
