The web browser serves as a gateway to the internet, which has become the primary platform for professional activities in contemporary society. However, accessing this gateway poses significant risks due to numerous threats that exist online, such as malware, intrusive pop-up advertisements, cryptocurrency mining software, and fraudulent websites. Compounding these dangers is the fact that all leading web browsers are typically set up by default to prioritise optimal performance, compatibility, and user convenience. Furthermore, users frequently exacerbate these risks by neglecting essential safety protocols associated with web browsing best practices.
Ensure Your Web Browser is Up-to-Date
Leading web browsers such as Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, and Google Chrome are routinely updated to address bugs, introduce new features, and, most critically, rectify security vulnerabilities. For instance, in 2022, Google Chrome—recognised as the most widely used web browser—saw the release of a significant new version approximately every month, accompanied by several minor updates in between. It is advisable to promptly install any available updates for your web browser upon notification of a new version. This proactive measure is essential in safeguarding against the potential exploitation of security weaknesses present in your current browser version by cyber criminals.
Minimise the Use of Browser Extensions
Occasionally, a significant number of users find themselves at risk after downloading harmful web browser extensions. For example, in 2020, the cybersecurity company Avast identified 28 extensions that were embedded with code capable of executing various malicious actions. These particular extensions had been installed by over three million individuals, thereby exposing them to risks such as phishing attacks, malware infections, and data breaches. While web browser extensions can provide considerable utility, it is advisable to limit their installation. This caution arises from the fact that any developer may face security vulnerabilities. When multiple extensions are available that serve similar purposes, it is prudent to select one that has a proven track record and has garnered numerous favorable reviews.

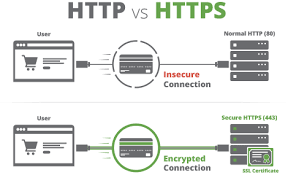
Activate HTTPS-Only Mode
HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is a protocol utilised for secure communication across computer networks, primarily the Internet. Nearly all trustworthy websites today employ HTTPS to encrypt data during transmission, and leading web browsers offer a feature to activate HTTPS-only mode, assisting users in steering clear of unsecured websites.
For Firefox: Navigate to Settings, proceed to Privacy & Security, locate the HTTPS-Only Mode setting, activate it, and then restart your browser.
For Edge: Access edge: flags, enable the Automatic HTTPS flag, and restart your browser.
For Chrome: Open Settings, go to Privacy and Security, select Security, turn on the Always Use Secure Connections option, and restart your browser.
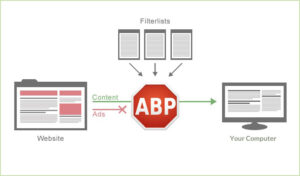
Adblocker
One essential web browser extension to consider is an adblocker, such as uBlock Origin, which is compatible with various browsers, including Chrome, Chromium, Edge, Firefox, Opera, and Pale Moon. Adblockers often spark debate among users, as many opt to install them in order to eliminate advertisements from websites for a more pleasant reading or viewing experience. However, it is essential to note that adblockers do not solely target legitimate advertisements that generate revenue for websites; they also obstruct harmful ads, numerous irritants, privacy risks, trackers, and additional threats. The most effective ad blockers provide options for customisation regarding what content to block, allowing users the discretion to determine which websites they wish to support by permitting the display of ads.
Disabling Pop-Up Windows
Pop-up windows not only pose an irritation but also represent a significant security risk, as they can redirect users to harmful websites and are often programmed to appear directly beneath the mouse cursor. Fortunately, major web browsers offer built-in capabilities to block these pop-ups without the need for external extensions:
– Firefox: Access the Settings menu, select the Privacy & Security section, and ensure that the option to Block pop-up windows is activated.
– Edge: Open the Settings menu, utilise the search function to locate the pop-ups and redirects setting, select the relevant category, and confirm that it is enabled.
– Chrome: Navigate to Settings, proceed to Privacy and Security, then Site Settings; open the Pop-ups and Redirects category and verify that the option preventing sites from sending pop-ups or employing redirects is enabled.
While numerous third-party extensions are available for blocking pop-up windows, they are typically unnecessary unless one frequently encounters websites that deliberately generate such interruptions.
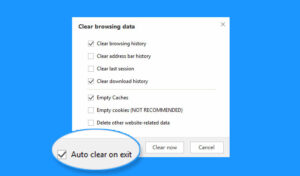
Remove Unnecessary Cookies
Cookies are small data files utilised by websites to store information regarding individual user sessions, thereby facilitating personalised experiences. Certain websites employ a specific category of cookies known as tracking cookies, which monitor users’ online behaviour. To safeguard your privacy and prevent tracking through cookies, it is advisable to eliminate all cookies except those linked to trusted and frequently visited sites. While third-party extensions such as Click&Clean can simplify this process, most major web browsers include built-in cookie management features that negate the need for additional software.
In conjunction with managing cookies, it is prudent to activate the Do Not Track setting in your web browser to signal your preference against being monitored by websites. The following instructions detail how to enable this feature across various browsers:

– Firefox: Access Settings, select the Privacy & Security panel, locate the Enhanced Tracking Protection section, and opt for Always under the option to send a Do Not Track signal indicating that you do not wish to be tracked.
– Edge: Open Settings and utilise the search bar to find the Send Do Not Track requests option; then enable this feature.
– Chrome: Navigate to Settings, proceed to Privacy and Security, select Cookies and other site data, and activate the option that sends Do Not Track requests with your browsing activity.
Employ a Password Manager Extension
In recent times, major web browsers have integrated password management features, enabling users to securely store frequently used passwords for more efficient login processes. While these built-in password management tools are beneficial, they are significantly outperformed by dedicated password manager extensions such as Bitwarden, LastPass, or 1Password. These extensions facilitate seamless access to saved passwords across various devices and platforms and provide enhanced security measures through the implementation of multiple multi-factor authentication options.
Deactivate the Autofill Functionality
The Autofill functionality is designed to simplify your experience by automatically filling in form fields with previously stored data, such as addresses, passwords, and credit card information. While this feature can be beneficial, it also poses significant risks; it facilitates the easy entry of sensitive data into forms potentially created by malicious actors. Additionally, any saved information can be accessed by anyone who has access to your device. If the advantages of using Autofill do not sufficiently outweigh the associated security risks while browsing online, it is advisable to deactivate this feature. This can be accomplished by adjusting a single setting in your browser:
– Firefox: Navigate to Settings, select the Privacy & Security panel, locate the Forms and Autofill section, and turn off the Autofill addresses option.
– Edge: Open Settings, select the Profiles tab, access the Personal info category, and turn off the Save and Fill Custom Info feature.
– Chrome: Go to Settings, select the Autofill tab, and turn off all autofill options.
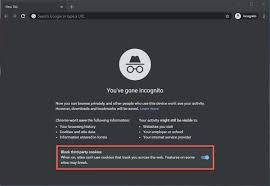
Utilize Private Browsing
Private browsing, often referred to as incognito mode, is a feature that is frequently misunderstood. Many individuals assume its primary function is to conceal their online activities; however, this needs to be more accurate. In reality, private browsing erases all data related to your session—including history, downloads, and cookies—upon closing the private window. Additionally, some web browsers implement stringent tracking prevention measures when this mode is activated. This feature proves particularly beneficial when accessing online accounts on shared or public computers. It can also be advantageous for visiting websites where you prefer not to retain cookies on your device.

Employ a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
When you access a website through your web browser, your internet service provider can monitor your online activities, the administrator of the local network to which you are connected, and potentially even harmful individuals if the network lacks adequate security. To safeguard your online privacy from these third parties, it is advisable to route your web browser traffic through a virtual private network (VPN). This technology provides an encrypted connection for web browsing, allowing for secure data transmission over the public internet. Additionally, a VPN can mask your actual IP address and create the appearance that you are accessing the internet from another country. This feature can be particularly beneficial while travelling, as many online services activate security protocols upon detecting login attempts from unfamiliar locations.

Tips for a Safer Browsing Experience on Maxthon Browser
1. Update Regularly: Ensure your Maxthon browser is up-to-date. Regular updates often include security patches that protect against the latest vulnerabilities.

2. Enable Security Features: Activate built-in security features, such as phishing protection and malicious website blocking. These options are in the settings menu under Security.
3. Use Private Browsing Mod*: For sensitive tasks, switch to private browsing mode. This feature prevents your browsing history from being saved and helps maintain confidentiality.
4. Install Extensions Carefully: Be cautious when adding extensions or plugins. Only download them from trusted sources to avoid malware or adware infections.
5. Manage Cookies: Adjust your cookie settings to limit tracking by websites. Consider setting it only to accept essential cookies while blocking third-party cookies.
6. Utilize the VPN Feature: If available, use Maxthon’s built-in VPN service for added privacy and security while browsing on public networks.
7. Be Wary of Pop-Ups: Enable pop-up blockers to reduce unwanted ads and potential phishing attempts that could compromise your personal information.
8. Secure Your Passwords: To enhance account security, use a password manager integrated with Maxthon or create strong, unique passwords for different sites.
9. Educate Yourself on Phishing Scams: Stay informed about common phishing tactics and suspicious links before clicking on any unfamiliar emails or messages.
10. Backup Your Data: Regularly back up your bookmarks and essential data from the browser to ensure you don’t lose access in case of an unexpected issue.