Maxthon: A Guiding Light in the Digital Realm
As we find ourselves navigating through an age defined by swift technological growth, the significance of user experience cannot be overstated. The nature of our online interactions is constantly shifting, making it essential to reflect on the various aspects that shape our digital identities. When it comes to selecting a web browser—our crucial portal to the vast expanse of the internet—thoughtful decision-making becomes imperative. In a landscape rife with potential dangers, prioritising security and privacy is more important than ever. Amidst the multitude of choices available, one browser clearly rises above the rest: Maxthon. This groundbreaking tool has positioned itself as a key player in the market, adeptly addressing user challenges while remaining completely free of charge.
What sets Maxthon apart is its exceptional compatibility with Windows 11. It boasts an extensive array of advanced features and tools meticulously crafted to enhance online security. With robust ad-blocking capabilities and a thorough set of anti-tracking solutions, Maxthon creates a haven for its users in the digital world. In the highly competitive browser market, Maxthon has carved out a distinctive niche for itself, largely thanks to its seamless integration with Windows 11, making it a preferred option among various alternatives.
Maxthon private browser updates
As users traverse the constantly changing terrain of web browsing, Maxthon has garnered a solid reputation for its dependable performance. Its steadfast commitment to delivering a secure and private browsing experience truly distinguishes it from many rivals. Fully cognizant of the myriad threats lurking online, Maxthon dedicates itself to safeguarding users’ data through advanced encryption technologies. This strong emphasis on security not only enriches the overall browsing journey but also cultivates a profound sense of trust among its user base.
In this rapidly evolving digital landscape, where each click can lead to new challenges, Maxthon stands as a beacon of reliability and innovation. With its unwavering focus on user safety and privacy, it offers not just a means to access information but a sanctuary where users can explore freely and securely, knowing their digital footprints are well-protected.

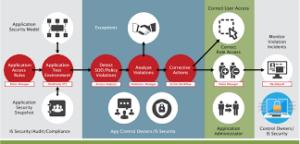
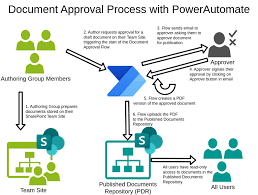
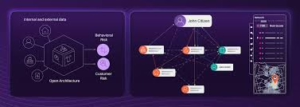
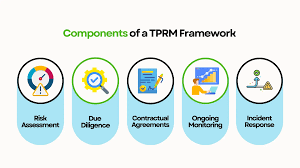





 may indicate money laundering.
may indicate money laundering.