Key Insights:

- Luxury car sales in Singapore have dramatically dropped, with some brands seeing sales decline by up to 75% in 2024 compared to 2023.
- The decline is primarily attributed to two main factors:
- A major $2 billion money-laundering scandal involving Chinese nationals
- Increased government taxes on luxury vehicles
Sales Decline Details:
- Rolls-Royce: Sales dropped from 95 to 23
- Ferrari: Sales fell from 97 to 29
- Jaguar: Sales nearly halved to 27
- Bentley: Sales decreased from 58 to 25

Context of the Scandal:
- In a 2023 police raid, 77 vehicles were seized
- At one property, four cars worth S$4.7 million (US$3.5 million) were confiscated
- 10 individuals linked to a gang from China’s Fujian province were sentenced
Market Shifts:
- Luxury car dealers report customers wanting to keep a lower profile
- Electric vehicle (EV) sales have surged
- BYD (Chinese manufacturer) became the second top-selling car brand
- BYD sales increased fourfold to 6,191 in 2024
- Tesla sales more than doubled to 2,384
Government Actions:
- Increased taxes on expensive cars (from 220% to 320% for cars over S$80,000)
- Mandated stricter due diligence for luxury car, property, and gemstone sales
- Selling off confiscated vehicles (33 cars sold so far)

The article highlights how a money-laundering scandal and government regulations have significantly reshaped Singapore’s luxury car market, pushing buyers towards more discreet and electric vehicle options.
Singapore’s Anti-Money Laundering Approach
Key Components of Prevention
1. Regulatory Oversight

- Extensive due diligence requirements for high-value transactions
- Mandatory reporting of suspicious financial activities
- Cross-sector monitoring (luxury cars, real estate, gemstone sales)
2. Enforcement Mechanisms
- Proactive law enforcement investigations
- Significant asset seizure capabilities
- Willingness to prosecute complex international financial crimes

3. Specific Sector Controls
Luxury Goods Sector
- Mandatory source of financing checks
- Reporting requirements for high-value purchases
- Increased scrutiny of transactions involving foreign nationals
Automotive Industry
- High taxation on luxury vehicles (320% for cars over S$80,000)
- Certificate of Entitlement System Limiting Vehicle Purchases
- Detailed customer background checks
Recent Major Case Study

2023 Money Laundering Investigation
- Scale: Approximately $2 billion in illicit funds
- Targets: Individuals linked to a Chinese provincial gang
- Enforcement Actions:
- 77 vehicles seized
- 10 individuals sentenced
- Systematic asset confiscation and resale
Deterrence Strategies
- High-profile prosecutions
- Significant financial penalties
- Reputational consequences for involved parties
- Transparent reporting of enforcement actions

Emerging Trends
- Increased focus on digital financial transactions
- Enhanced international cooperation
- Technological integration in financial monitoring
- Adaptable regulatory frameworks

Challenges
- Balancing strict controls with the attractive business environment
- Managing complex cross-border financial flows
- Keeping pace with evolving money laundering techniques

.
Identity Theft
Identity theft is a pervasive form of fraud that can have devastating consequences for victims. In this crime, the perpetrator steals an individual’s personal information to assume their identity. This stolen information can often be gathered from discarded documents such as bank statements, utility bills, or even phishing scams.
Once armed with this data, the criminal may choose to open accounts in the victim’s name, a process known as application fraud. They might apply for credit cards, loans, or utility services under pretences, leaving the unsuspecting victim to deal with the aftermath.
The emotional toll of identity theft can be immense. Victims often face financial losses and damage to their credit scores, which can take years. In today’s digital age, account takeovers have become a prevalent threat to unsuspecting victims. Criminals typically employ tactics such as phishing, vishing, or smishing to manipulate individuals into revealing their personal information.

Phishing often involves deceptive emails that appear to come from legitimate sources. These emails may prompt the victim to click on malicious links or provide sensitive details under the guise of verifying their identity.
Vishing, or voice phishing, involves phone calls in which scammers impersonate bank representatives or trusted entities to extract confidential information directly from the victim. Similarly, smishing involves text messages that lure individuals into divulging critical data.
Once armed with this personal information, the criminal can easily convince a bank to change the account holder’s address. This deception allows them full access to the victim’s financial accounts and resources.

Additionally, some criminals are skilled enough to bypass bank interaction altogether. They can use the obtained credentials to log into online accounts directly, executing unauthorised transactions without needing any further verification.
The consequences for victims can be devastating, leading not only to financial loss but also emotional distress as they recover their stolen identities and secure their accounts. Consequently, individuals must remain vigilant and understand these risks to protect themselves against potential account takeovers for repair. Additionally, they may find themselves tangled in legal disputes as they try to prove their innocence.

Recovering from such a violation requires diligence and time, making it crucial for individuals to safeguard their personal information vigilantly. Implementing measures like shredding sensitive documents and monitoring credit reports can help prevent these types of crimes before they occur.
Maxthon
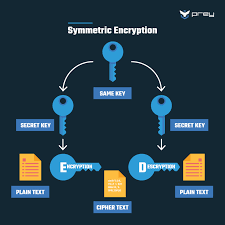
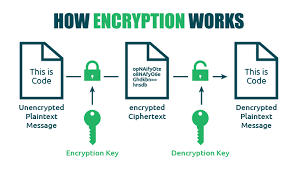
Maxthon has set out on an ambitious journey aimed at significantly bolstering the security of web applications, fueled by a resolute commitment to safeguarding users and their confidential data. At the heart of this initiative lies a collection of sophisticated encryption protocols, which act as a robust barrier for the information exchanged between individuals and various online services. Every interaction—be it the sharing of passwords or personal information—is protected within these encrypted channels, effectively preventing unauthorised access attempts from intruders.
 This meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
This meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
In today’s rapidly changing digital environment, Maxthon’s unwavering commitment to ongoing security enhancement signifies not only its responsibility toward users but also its firm dedication to nurturing trust in online engagements. With each new update rolled out, users can navigate the web with peace of mind, assured that their information is continuously safeguarded against ever-emerging threats lurking in cyberspace.