Bank Jago, an Indonesian digital bank with over 14 million customers (as of Q3 2024), has formed a multi-year collaboration with Google Cloud to enhance its banking operations through advanced data analytics and AI.

The partnership involves:
- Using Google Cloud’s BigQuery and Vertex AI platforms to improve customer experiences and streamline operations
- Leveraging Google Cloud’s secure infrastructure to scale digital services efficiently
- Implementing generative AI applications, including:
- Fraud detection tools that analyze transaction patterns in real time
- Customer sentiment analysis tools
- AI coaching tools for contact center agents
Bank Jago is also utilizing Vertex AI Pipelines to standardize workflows for validating AI solutions and Vertex AI Model Registry to centralize approved AI models, which helps accelerate development while mitigating risks.

This partnership represents a continuation of their relationship, as Bank Jago has been using Google Cloud’s infrastructure since 2021. The bank is now moving toward a platform-based approach to implement enterprise-grade generative AI solutions responsibly and efficiently.
Analysis of Bank Jago’s Google Cloud Adoption for Workflow Enhancement
Bank Jago’s partnership with Google Cloud represents a strategic move to transform its workflow and operational efficiency. Here’s an analysis of the key aspects:

Strategic Implementation
Bank Jago is leveraging Google Cloud’s capabilities in several interconnected ways:
- Data Infrastructure Upgrade: Moving to BigQuery allows Bank Jago to consolidate and analyze large volumes of customer data more efficiently than traditional database systems.
- AI Integration: Implementing Vertex AI provides a foundation for developing and deploying machine learning models that can automate complex processes.
- Platform-Based Approach: Rather than developing siloed solutions, Bank Jago is adopting a comprehensive platform strategy that enables consistent AI application across different business functions.

Workflow Enhancements
The partnership explicitly enhances Bank Jago’s workflows through:
- Automated Fraud Detection: Real-time transaction pattern analysis reduces manual review processes and speeds up fraud identification.
- Streamlined Customer Service:
- The sentiment analysis tools help prioritize customer interactions
- AI coaching tools improve agent training and performance assessment
- These reduce training time and improve consistency in customer interactions
- Standardized AI Development: Vertex AI Pipelines create consistent workflows for validating AI solutions, reducing development friction and ensuring quality standards.
- Centralized Model Management: The Model Registry creates a single source of truth for approved AI models, eliminating duplicate efforts and inconsistent implementations.

Business Impact
This technological adoption likely delivers several business benefits:
- Operational Efficiency: Reducing manual processes and standardizing workflows across the organization.
- Scalability: The cloud infrastructure enables Bank Jago to handle their growing customer base (14 million and expanding) without proportional increases in operational costs.
- Innovation Acceleration: The standardized AI development pipeline allows faster deployment of new financial solutions.
- Risk Management: Improved fraud detection and consistent model governance help mitigate financial and regulatory risks.
This partnership represents a comprehensive technological transformation rather than just a tool implementation, positioning Bank Jago to operate more efficiently in Indonesia’s competitive digital banking landscape.
.
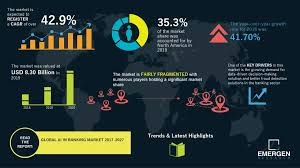
AI in Banking: Themes, Challenges, and Implementation Strategies
Major Themes
1. Transformative Potential

- Unprecedented economic opportunity: Potential to boost annual operating profits by £200bn-£340bn
- Comprehensive digital transformation across banking operations
- Shift from traditional banking models to AI-driven, data-centric approaches
2. Strategic Implementation

- Methodical, Phased Transformation Approach
- Compared to steering an “oil tanker” – requiring careful, calculated changes
- Systematic rebuilding of technological architecture
3. Regulatory Compliance and Governance

- Increasing regulatory scrutiny (e.g., EU AI Act)
- Focus on:
- Robust risk management
- Data governance
- Transparency in AI systems
- Human oversight
Key Challenges
1. Data Management
- Fragmented data across multiple systems
- Lack of a Single Source of Truth (SSOT)
- Difficulty in consolidating and standardizing information

2. Technological Integration
- Replacing legacy systems
- Ensuring seamless AI integration
- Managing complex technological transitions

3. Organizational Culture
- Resistance to change
- Need for comprehensive staff training
- Developing AI literacy across the organization
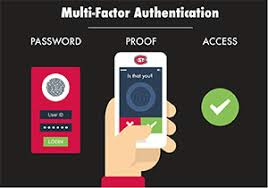
4. Trust and Security
- Maintaining customer confidence
- Balancing innovation with data protection
- Demonstrating transparent and ethical AI use
Implementation Strategies
1. Phased Transformation Approach

- Incremental system upgrades
- Component-by-component modernization
- Controlled risk management
2. Governance Frameworks
- Establish AI governance boards
- Create comprehensive oversight mechanisms
- Develop transparent
 AI use case evaluation processes
AI use case evaluation processes
3. Data Strategy
- Implement open banking principles
- Develop robust data management protocols
- Ensure data quality and standardization

4. Customer-Centric Implementation
- Focus on enhancing customer experience
- Leverage AI to improve service efficiency
- Maintain transparency and build trust
- Practical AI Applications in Banking


1. Customer Service
- AI-enabled contact centers
- Enhanced customer interaction capabilities
- Improved problem resolution efficiency

2. Operational Optimization
- Automated data cleaning
- Testing framework improvements
- Code generation for platform development

3. Risk Management
- Advanced loan and mortgage approval processes
- Intelligent risk assessment
- Regulatory compliance monitoring

Future Outlook
- Continuous adaptation of AI systems
- Emphasis on resilience and flexibility
- Integration of advanced AI with robust security measures

Conclusion
Successful AI implementation in banking requires a holistic approach that balances technological innovation, regulatory compliance, organizational culture, and customer trust.

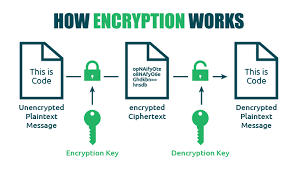
How Encryption Works

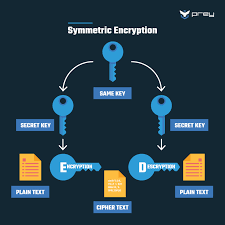
Encryption uses mathematical algorithms to convert plaintext (readable data) into ciphertext (scrambled data). Only those with the decryption key can convert the ciphertext back into usable information. There are two main types:
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. It’s efficient but requires a secure key exchange.
- Asymmetric Encryption uses a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption—to allow secure communication without prior key exchange.
Key Encryption Applications for Privacy
Device Encryption
- Full-disk encryption: Protects all data on your computer or smartphone (BitLocker for Windows, FileVault for Mac, built-in encryption for iOS and Android)
- File-level encryption: Protects individual files and folders

Communication Encryption
- HTTPS: Secures website connections (look for the padlock icon in your browser)
- End-to-end encryption: Used in messaging apps like Signal, WhatsApp, and others to ensure only you and your recipient can read messages
- Email encryption: Options include PGP (Pretty Good Privacy), S/MIME, or encrypted email services
Network Encryption
- VPNs: Create an encrypted tunnel for all your internet traffic
- Wi-Fi encryption: WPA3 is the current most substantial standard for wireless networks
Cloud Storage Encryption
- At-rest encryption: Protects stored data
- Zero-knowledge encryption: The provider has no access to your encryption keys
- Client-side encryption: Data is encrypted before leaving your device

Implementing Encryption in Your Digital Life
- Enable device encryption on all your computers and mobile devices
- Use encrypted messaging apps for sensitive communications
- Verify HTTPS connections when sharing personal or financial information
- Consider encrypted email for sensitive communications
- Choose cloud services with strong encryption policies
- Use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks
- Password-protect and encrypt sensitive files and backups
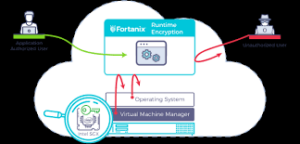
Limitations to Consider
- Encryption can’t protect against malware already on your device
- Weak passwords can undermine even the strongest encryption
- Encryption doesn’t hide metadata (who you’re communicating with, when, how often)
- Some countries have laws limiting encryption use or requiring backdoors

Encryption is a fundamental aspect of digital privacy that works best as part of a comprehensive security strategy. By understanding and implementing appropriate encryption methods, you can significantly enhance your online privacy protection.
.
Identity Theft
Identity theft is a pervasive form of fraud that can have devastating consequences for victims. In this crime, the perpetrator steals an individual’s personal information to assume their identity. This stolen information can often be gathered from discarded documents such as bank statements, utility bills, or even phishing scams.
Once armed with this data, the criminal may choose to open accounts in the victim’s name, a process known as application fraud. They might apply for credit cards, loans, or utility services under pretences, leaving the unsuspecting victim to deal with the aftermath.
The emotional toll of identity theft can be immense. Victims often face financial losses and damage to their credit scores, which can take years. In today’s digital age, account takeovers have become a prevalent threat to unsuspecting victims. Criminals typically employ tactics such as phishing, vishing, or smishing to manipulate individuals into revealing their personal information.

Phishing often involves deceptive emails that appear to come from legitimate sources. These emails may prompt the victim to click on malicious links or provide sensitive details under the guise of verifying their identity.
Vishing, or voice phishing, involves phone calls in which scammers impersonate bank representatives or trusted entities to extract confidential information directly from the victim. Similarly, smishing involves text messages that lure individuals into divulging critical data.
Once armed with this personal information, the criminal can easily convince a bank to change the account holder’s address. This deception allows them full access to the victim’s financial accounts and resources.

Additionally, some criminals are skilled enough to bypass bank interaction altogether. They can use the obtained credentials to log into online accounts directly, executing unauthorised transactions without needing any further verification.
The consequences for victims can be devastating, leading not only to financial loss but also to emotional distress as they recover their stolen identities and secure their accounts. Consequently, individuals must remain vigilant and understand these risks to protect themselves against potential account takeovers for repair. Additionally, they may find themselves tangled in legal disputes as they try to prove their innocence.

Recovering from such a violation requires diligence and time, making it crucial for individuals to safeguard their personal information vigilantly. Implementing measures like shredding sensitive documents and monitoring credit reports can help prevent these types of crimes before they occur.
Maxthon
Maxthon has set out on an ambitious journey aimed at significantly bolstering the security of web applications, fueled by a resolute commitment to safeguarding users and their confidential data. At the heart of this initiative lies a collection of sophisticated encryption protocols, which act as a robust barrier for the information exchanged between individuals and various online services. Every interaction—be it the sharing of passwords or personal information—is protected within these encrypted channels, effectively preventing unauthorised access attempts from intruders.
 This meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
This meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
In today’s rapidly changing digital environment, Maxthon’s unwavering commitment to ongoing security enhancement signifies not only its responsibility toward users but also its firm dedication to nurturing trust in online engagements. With each new update rolled out, users can navigate the web with peace of mind, assured that their information is continuously safeguarded against ever-emerging threats lurking in cyberspace.
