Personal Device Security

Smartphone Security Measures
- Non-jailbreaking policy: Fundamental in Singapore, where smartphone penetration exceeds 90% of the population
- Auto-lock and biometric authentication: Aligns with Singapore’s Smart Nation initiatives, promoting secure digital interactions
- Software updates: Critical for Singapore users who typically keep smartphones for 21-24 months
- Two-factor authentication: This complements Singapore’s SingPass authentication system, which already implements 2FA
Application to Singapore: The Singapore Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) requires individuals to reasonably protect personal data. These measures help Singapore residents comply with national expectations for data security.


Network Security
VPN Implementation
- Encryption benefits: Essential in Singapore, where public Wi-Fi is abundant (malls, MRT stations, libraries)
- Server selection: Singapore users should consider that local VPN servers provide better speed but international servers offer additional privacy from regional surveillance
- Legal considerations: Singapore has strict cybersecurity laws, so users should choose VPNs that comply with local regulations
Application to Singapore: The Cybersecurity Act 2018 emphasizes protecting Critical Information Infrastructure. VPNs complement this national focus on secure communications for individuals.

Digital Identity Protection
Identity Monitoring Services
- Dark web monitoring: Valuable as Singapore consistently ranks among countries with lowest cybercrime rates, making residents potential targets for international operations
- Credit monitoring: This should be adapted to Singapore’s credit reporting agencies (DP Credit Bureau)
- Insurance coverage: Identity theft insurance should align with Singapore dollar valuations and local financial regulations
Application to Singapore: Singapore’s emphasis on digital government services makes identity protection particularly important as citizens increasingly use digital identities for official transactions.
Authentication Management

Password Management Systems
- Password generators: Help meet the complexity requirements of the Singapore government and financial portals
- Secure storage: Supports compliance with Singapore’s cybersecurity guidelines for the storage of authentication information
- Cross-device synchronization: Important for Singapore’s high multi-device ownership rates
Application to Singapore: Singapore’s move toward digital banking licenses and expansion of digital financial services makes robust password management increasingly critical.

Website Safety Verification
Security Protocol Verification
- HTTPS checking: Critical for Singapore’s growing e-commerce market
- Payment method verification: Aligns with Singapore’s push for cashless solutions
- Domain verification: Helps identify legitimate Singapore business domains (.sg, .com.sg)
Application to Singapore: The Cybersecurity Agency of Singapore (CSA) regularly warns about phishing campaigns targeting Singaporeans. These verification methods help residents follow CSA guidelines.
Legal and Regulatory Context
Singapore’s cybersecurity framework is particularly robust:
- The Cybersecurity Act 2018 provides comprehensive regulatory oversight
- The Computer Misuse Act has been updated to address modern cyber threats
- The PDPA establishes clear obligations for data protection
Strategic Importance: For Singapore residents, cybersecurity is not just about personal protection but contributes to national security objectives, as Singapore has identified cybersecurity as a pillar of its defense strategy.

Singapore-Specific Recommendations
- SingPass Protection: Apply multi-factor authentication and regular password updates for this national digital identity system
- Banking Security: Use bank-provided security tokens and authentication apps widely implemented by Singapore banks
- Regular CSA Monitoring: Follow alerts from the Cybersecurity Agency of Singapore about current threats
- ScamShield App: Consider using this government-developed app that blocks scam calls and messages
- Report Cybercrime: Utilize Singapore Police Force’s online reporting system for cybercrime incidents
These measures, when implemented together, provide a comprehensive cybersecurity approach tailored to Singapore’s digital ecosystem and regulatory environment.
Types of Cybercrime: Singapore Context and Countermeasures

Key Cybercrime Types and Their Singapore Relevance
1. Phishing Scams
Global Context: Phishing involves deceptive communications designed to trick victims into revealing personal or corporate information through social engineering tactics.

Singapore Application: Singapore has seen a significant rise in phishing incidents, with the Singapore Police Force reporting that scam cases hit a record high in 2023-2024. Local phishing schemes often impersonate trusted entities like:
- Government agencies (SingPass, CPF, IRAS)
- Banks and financial institutions (DBS, OCBC, UOB)
- E-commerce platforms (Shopee, Lazada)
- Logistics companies (SingPost, Ninja Van)

2. Identity Theft
Global Context: Criminals obtain personal information to conduct unauthorized transactions or other fraudulent activities.
Singapore Application: Singapore’s high digital adoption rate and concentrated wealth make it an attractive target. Common manifestations include:
- Unauthorized bank transactions
- Credit card fraud
- Creation of fraudulent accounts using stolen NRIC details
- SingPass credential theft enabling access to multiple government services

3. Ransomware Attacks
Global Context: Malicious software encrypts victims’ files and demands payment for restoration.
Singapore Application: Singapore businesses and institutions have faced targeted ransomware campaigns with high-profile cases, including:
- Healthcare sector attacks affecting patient data
- SME targeting that exploits limited cybersecurity resources
- Supply chain vulnerabilities in Singapore’s role as a global logistics hub

4. DDoS Attacks
Global Context: These attacks overwhelm systems with excessive traffic, causing service outages.
Singapore Application: As a financial and technological hub, Singapore faces DDoS threats targeting:
- Financial services infrastructure
- Government digital services
- Critical information infrastructure
- Tech company operations

Countermeasures in the Singapore Context
1. Legal and Regulatory Framework
- Cybersecurity Act (2018): Establishes a framework for the protection of Critical Information Infrastructure
- Computer Misuse Act: Criminalizes unauthorized access and other cyber offenses
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA): Governs collection, use, and disclosure of personal data
- Cybersecurity Labeling Scheme (CLS): Rates IoT devices on security levels

2. National Initiatives
- Singapore Cyber Security Agency (CSA) leadership in national cybersecurity strategy
- SG Cyber Safe Programme to raise businesses’ cybersecurity awareness
- Singapore’s National Cybercrime Action Plan
- Digital Defense pillar of Total Defense framework

3. Technical Measures
- Advanced Threat Intelligence solutions tailored to Singapore’s threat landscape
- Multi-factor authentication mandatory for sensitive systems (like SingPass)
- Virtual Private Networks for secure remote connections
- Cybersecurity health checks for businesses
- Secure web gateways to filter malicious content

4. Education and Awareness
- Cybersecurity awareness campaigns (like CSA’s “Better Cyber Safe Than Sorry”)
- Scam Alert website and app providing real-time information on scams
- Digital Defense Badge program for students
- SME Go Digital program with cybersecurity components
- Industry-specific awareness training for high-risk sectors

5. Public-Private Partnerships
- Collaboration between government agencies, businesses, and academia
- Information sharing platforms like the Singapore Computer Emergency Response Team (SingCERT)
- Joint exercises to test cybersecurity preparedness
- Industry-specific security guidelines

Singapore-Specific Recommendations
- Implement Singapore’s SMS Sender ID Registry to reduce SMS phishing attacks.
- Adopt National Digital Identity solutions like SingPass Face Verification
- Participate in sector-specific threat sharing groups coordinated by CSA
- Implement the Cybersecurity Toolkit for SMEs developed by IMDA and CSA
- Regular employee training on Singapore-specific scam tactics
- Monitor government alerts from SingCERT and ScamShield
- Deploy AI-based threat detection systems calibrated to local threat patterns
- Conduct regular security assessments aligned with MAS/IMDA guidelines
- Engage with Singapore Security Operations Centres (SOCs) for continuous monitoring
- Develop incident response plans compliant with local regulatory requirements

- Keep devices updated: Regularly update your computer and mobile devices to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use security software: Install antivirus and anti-malware protection on your computers and schedule regular scans.
- Practice good password habits: Create strong, unique passwords for each account, enable multi-factor authentication, and avoid sharing passwords.
- Secure your home network: Set strong Wi-Fi passwords, use proper encryption (at least WPA2), update router software, and consider hiding your network.
- Defend against phishing/vishing: Be vigilant about suspicious emails or calls requesting personal information, and verify legitimacy through official channels.
- Back up your data: To recover from potential compromises, regularly copy files to external storage or secure cloud services.
- Educate family members: Discuss internet security with children and older relatives who may be vulnerable to different types of cyber tricks.
- Prevent identity theft: Shred sensitive documents, avoid suspicious links, and regularly review your credit report.
- Know what to do if victimized: Consider enabling fraud alerts or credit freezes if your information is compromised.
- Control your information: Be cautious about sharing sensitive information online and regularly review privacy settings.
According to the article, the global financial impact of cyber fraud is rising dramatically, with victims losing $37.4 billion to cybercriminals in the past five years. Phishing scams are the most common, while investment scams are the costliest (over $4.5 billion lost in 2023).

The article also mentions that scammers are increasingly using AI tools like deepfakes and large language models to create more sophisticated fraud attempts.

Crime Prevention Methods
Crime prevention encompasses a variety of strategies designed to reduce criminal activity by addressing its root causes and opportunities. Here are the main approaches to crime prevention:
Situational Crime Prevention
These methods focus on reducing opportunities for crime by making criminal acts more difficult and risky:
- Target hardening: Using physical barriers like locks, alarms, and security systems to protect property
- Access control: Limiting entry to specific areas through key cards, security gates, or doormen
- Natural surveillance: Designing spaces to increase visibility (better lighting, removing visual obstructions)
- CCTV and surveillance: Installing cameras and monitoring systems to deter criminals and collect evidence
- Environmental design: Using CPTED (Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design) principles to create safer spaces

Social Crime Prevention
These strategies address the underlying social factors that contribute to crime:
- Education and awareness programs: Teaching people about risks and prevention strategies
- Community engagement: Neighborhood watch programs, community policing initiatives
- Youth intervention programs: After-school activities, mentoring, and education to provide positive alternatives
- Economic opportunity development: Job training, employment programs, and economic revitalization
- Family support services: Counseling, parenting classes, and support for at-risk families

Law Enforcement Strategies
Proactive approaches by police and criminal justice systems:
- Hot spot policing: Concentrating resources in high-crime areas
- Problem-oriented policing: Identifying and addressing specific crime problems
- Intelligence-led policing: Using data analysis to predict and prevent crime
- Swift and inevitable consequences: Ensuring quick and consistent responses to criminal behaviour
- Focused deterrence: Targeting specific criminal behaviours with enhanced enforcement

Technological Prevention
Using technology to prevent various types of crime:
- Cybersecurity measures: Firewalls, anti-virus software, encryption, and multi-factor authentication
- Biometric security: Fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and other identity verification methods
- Smart home security: Internet-connected security systems that can be monitored remotely

- Location tracking: GPS monitoring for high-risk offenders
- Data analytics: Using big data to identify patterns and predict potential criminal activity
Individual Prevention Measures
Steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Personal awareness: Being alert to surroundings and potential dangers
- Target removal: Not displaying valuables, securing personal information
- Routine adjustments: Varying routes and schedules to avoid predictability
- Self-defence training: Learning physical defence techniques and situational awareness
- Building social connections: Developing networks of neighbours who watch out for each other
Each approach has strengths and limitations, and the most effective crime prevention strategies employ multiple methods in coordination.

Crime Prevention Methods in Singapore
Singapore is known for its low crime rates and effective crime prevention strategies. Here’s how the various crime prevention methods are applied in the Singapore context:
Situational Crime Prevention in Singapore
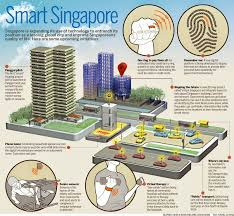
- Extensive CCTV network: Singapore has one of the world’s most comprehensive public surveillance systems, with over 90,000 police cameras installed across public housing estates, public areas, and transportation networks.
- Smart Nation initiatives: The government’s Smart Nation program includes sensors and surveillance technologies that enhance public safety.
- Housing design: HDB (Housing & Development Board) flats are designed with security features and community spaces that promote natural surveillance.
- Police cameras: The PolCam initiative places police cameras in public housing blocks and common areas to deter crime and aid investigations.
- Secured By Design: Commercial buildings and public facilities implement crime prevention through environmental design principles.
Social Crime Prevention in Singapore

- Community Policing: The Singapore Police Force’s Community Policing System divides neighbourhoods into smaller sectors with dedicated Neighborhood Police Centers.
- Citizens on Patrol: Volunteer residents patrol their neighbourhoods alongside police officers.
- Yellow Ribbon Project: Rehabilitation and reintegration programs for ex-offenders to reduce recidivism.
- Racial Harmony policies: Programs that promote social cohesion and reduce tensions between different ethnic groups.
- Education system: Schools incorporate character development and values education to promote law-abiding behaviour.

Law Enforcement Strategies in Singapore

- Swift and sure justice: Singapore’s criminal justice system is known for its efficiency and certainty of punishment.
- Deterrent sentencing: Relatively harsh penalties for crimes serve as strong deterrents.
- Low corruption: Strong anti-corruption measures ensure police integrity.
- Data-driven policing: The Police Intelligence Department uses analytics to identify crime patterns and deploy resources effectively.
- Community engagement: Regular community outreach by Neighborhood Police Centers helps build trust and gather intelligence.
Technological Prevention in Singapore
- National Digital Identity System: Singpass provides secure digital identification for government and financial services.
- Cybersecurity infrastructure: The Cyber Security Agency of Singapore coordinates national efforts to protect critical infrastructure.
- Police technology: Advanced tools like the POLCAM 2.0 with analytics capabilities and the i-Witness mobile app for citizens to report incidents.
- Smart lamp posts: As part of Smart Nation initiatives, lamp posts equipped with sensors and cameras enhance public safety.
- Cashless society initiatives: Reducing cash transactions helps prevent certain types of theft and robbery.

Individual Prevention Measures Promoted in Singapore
- SGSecure app: A mobile application that allows citizens to report suspicious activities and receive emergency alerts.
- Public education campaigns: Regular campaigns like “Low Crime Doesn’t Mean No Crime” remind citizens to remain vigilant.
- Crime prevention messaging: Frequent public service announcements about scams and new crime trends.
- Neighborhood watch groups: Resident committees and neighborhood watch groups in residential areas.
- Public transport safety: Campaigns educating commuters about safety measures and reporting mechanisms.
Unique Aspects of Singapore’s Approach
- Total Defence: A national ideology that includes social and psychological defense against crime.
- Multi-agency collaboration: Different government agencies work together on crime prevention.
- Strict regulations: Controls on weapons, drugs, and public disorder serve as preventative measures.
- Community involvement: Strong emphasis on citizen participation in crime prevention.
- Integrated approach: Combining strict enforcement with rehabilitation and social support.
Singapore’s success in maintaining low crime rates is attributed to this comprehensive, multi-faceted approach that combines strong enforcement with community engagement and technological innovation.
Secure browsing
When it comes to staying safe online, using a secure and private browser is crucial. Such a browser can help protect your personal information and keep you safe from cyber threats. One option that offers these features is the Maxthon Browser, which is available for free. It comes with built-in Adblock and anti-tracking software to enhance your browsing privacy.

Maxthon Browser is dedicated to providing a secure and private browsing experience for its users. With a strong focus on privacy and security, Maxthon employs strict measures to safeguard user data and online activities from potential threats. The browser utilises advanced encryption protocols to ensure that user information remains protected during internet sessions.
In addition, Maxthon implements features such as ad blockers, anti-tracking tools, and incognito mode to enhance users’ privacy. By blocking unwanted ads and preventing tracking, the browser helps maintain a secure environment for online activities. Furthermore, incognito mode enables users to browse the web without leaving any trace of their history or activity on the device.
Maxthon’s commitment to prioritising the privacy and security of its users is exemplified through regular updates and security enhancements. These updates are designed to address emerging vulnerabilities and ensure that the browser maintains its reputation as a safe and reliable option for those seeking a private browsing experience. Overall, Maxthon Browser offers a comprehensive set of tools and features aimed at delivering a secure and private browsing experience.
Maxthon Browser, a free web browser, offers users a secure and private browsing experience with its built-in Adblock and anti-tracking software. These features help to protect users from intrusive ads and prevent websites from tracking their online activities. The browser’s Adblock functionality blocks annoying pop-ups and banners, allowing for an uninterrupted browsing session. Additionally, the anti-tracking software safeguards user privacy by preventing websites from collecting personal data without consent.
By utilising the Maxthon Browser, users can browse the internet confidently, knowing that their online activities are shielded from prying eyes. The integrated security features alleviate concerns about potential privacy breaches and ensure a safer browsing environment. Furthermore, the browser’s user-friendly interface makes it easy for individuals to customise their privacy settings according to their preferences.
Maxthon Browser not only delivers a seamless browsing experience but also prioritises the privacy and security of its users through its efficient ad-blocking and anti-tracking capabilities. With these protective measures in place, users can enjoy the internet while feeling reassured about their online privacy.
In addition, the desktop version of Maxthon Browser works seamlessly with their VPN, providing an extra layer of security. By using this browser, you can minimise the risk of encountering online threats and enjoy a safer internet experience. With its combination of security features, Maxthon Browser aims to provide users with peace of mind while they browse.
Maxthon Browser stands out as a reliable choice for users who prioritise privacy and security. With its robust encryption measures and extensive privacy settings, it offers a secure browsing experience that gives users peace of mind. The browser’s commitment to protecting user data and preventing unauthorised access sets it apart in the competitive web browser market.
