Industry Approach to AI:
- Initial excitement about AI has evolved into a more cautious approach
- Recognizes that AI isn’t a universal solution but needs targeted implementation
- Many clients lack clear AI strategies or struggle with integration
Endava’s Philosophy:
- Promotes thoughtful, careful implementation of AI technologies
- Investing in understanding AI while
- maintaining caution
- Develops practical tools to simplify tasks like coding
- Learns from real-world applications
AI’s Potential in Banking:
- Most significant potential is in fraud management, shifting from reactive to predictive approaches
- AI can process large data sets to recognize patterns and predict potential fraud
- Human oversight remains essential for proper decision-making
Broader Context:
- Compares AI’s potential impact to the early internet, suggesting transformative effects across industries
AI in Global Payments: Key Trends Analysis
Based on the article about Matt Williamson’s insights and broader industry knowledge, here’s an analysis of AI trends in global payments:
Current Implementation Stage
- The industry has moved from initial AI hype to a more measured, practical approach
- Many financial institutions are in an exploratory phase rather than full implementation
- Organizations are struggling with integration challenges despite investing in AI technologies
Primary Use Cases
- Fraud Detection & Prevention:
- Shifting from reactive to predictive fraud management
- Pattern recognition across large datasets to identify potential threats
- Real-time analysis of transactions for immediate intervention
- Process Automation:
- Streamlining backend operations like reconciliation and settlements
- Reducing manual processing in compliance workflows
- Automating coding and development processes
- Customer Experience:
- Personalized payment experiences and recommendations
- Conversational interfaces for customer service
- Improved authentication methods balancing security and convenience
Implementation Challenges
- Integration with legacy banking infrastructure
- Regulatory compliance and risk management
- Need for human oversight to ensure appropriate decision-making
- Difficulty measuring ROI on AI investments
Strategic Approaches
- More organizations adopting cautious, targeted implementation strategies
- Focus on specific business problems rather than broad AI adoption
- Growing emphasis on partner ecosystems rather than building everything in-house
- Testing and learning from real-world applications
Future Outlook
- Potential for transformative impact similar to the internet revolution
- Increasing focus on explainable AI for regulatory compliance
- Greater integration of AI across the payment lifecycle
- Emergence of new business models powered by AI capabilities
Applying AI in Singapore’s Payment Ecosystem
Singapore offers unique opportunities for AI application in payments due to its advanced financial infrastructure and progressive regulatory environment. Here’s how AI trends in global payments specifically apply to Singapore:
Singapore’s Advantages for AI in Payments
- Strong Digital Infrastructure:
- High smartphone penetration (approximately 92%)
- Advanced 5G network deployment
- Tech-savvy population comfortable with digital payments
- Progressive Regulatory Framework:
- MAS (Monetary Authority of Singapore) supports fintech innovation through regulatory sandboxes
- AI Governance Framework provides ethical guidelines for AI deployment
- Singapore’s Fairness, Ethics, Accountability and Transparency (FEAT) principles for AI
- Government Initiatives:
- Smart Nation initiative promoting digital transformation
- National AI Strategy with a significant focus on financial services
- Public-private partnerships supporting AI development
Specific AI Applications in Singapore’s Payment Landscape
- Fraud Prevention:
- Real-time transaction monitoring leveraging Singapore’s centralized data infrastructure
- Multi-layered authentication systems using behavioral biometrics
- Cross-border transaction analysis through Singapore’s position as a regional hub
- Integration with National Systems:
- Enhancement of PayNow and SGQR unified payment systems using AI
- Potential AI augmentation of Singapore’s national digital identity system (SingPass)
- Optimization of FAST (Fast And Secure Transfers) system
- Customer Experience Innovation:
- Multilingual AI assistants catering to Singapore’s diverse population
- Personalized recommendations based on spending patterns in local context
- Seamless integration between payment methods and loyalty programs
Implementation Strategies for the Singapore Market
- Partnership Approach:
- Collaborate with local banks (DBS, OCBC, UOB) for distribution and trust
- Engage with government initiatives like IMDA’s AI and Data programs
- Join industry consortiums such as the Singapore Fintech Association
- Regulatory Compliance Focus:
- Ensure adherence to MAS guidelines on technology risk management
- Implement PDPA (Personal Data Protection Act) compliant data handling
- Develop explainable AI models that satisfy local regulatory requirements
- Localization Considerations:
- Account for Singapore’s unique multi-cultural context in AI training
- Address local payment preferences and behaviors
- Consider regional expansion opportunities using Singapore as a hub
AI Implementation for Banks in Singapore’s Payment Ecosystem
Singapore’s banks are uniquely positioned to leverage AI in payments due to their technological readiness and strong regulatory support. Here’s how banks in Singapore can effectively implement AI payment solutions:
Strategic Implementation Approach
- Phased Deployment Strategy:
- Begin with targeted AI use cases that address specific pain points
- Establish clear metrics for measuring success and ROI
- Scale successful implementations across other banking functions
- Create a centralized AI governance structure for consistency
- Integration with Existing Systems:
- Identify key integration points with core banking platforms
- Leverage APIs to enable AI functionality without significant system overhauls
- Ensure compatibility with national payment infrastructure (FAST, PayNow)
- Address data silos that could limit AI effectiveness
- Skills Development:
- Build internal AI competencies through training and hiring
- Establish centers of excellence for AI implementation
- Partner with local universities for talent pipeline development
- Create cross-functional teams combining banking and AI expertise
Priority AI Applications for Singapore Banks
- Customer-Facing Solutions:
- Intelligent chatbots supporting multiple languages (English, Mandarin, Malay, Tamil)
- Personalized financial insights and spending analysis
- Voice-enabled payment authorizations
- Real-time transaction categorization and budget recommendations
- Risk Management & Security:
- Advanced fraud detection using behavioral analytics
- Credit risk assessment incorporating alternative data sources
- Anti-money laundering pattern detection
- Enhanced customer authentication combining biometrics and behavior
- Operational Efficiency:
- Automated payment reconciliation and exception handling
- Intelligent document processing for payment-related forms
- Smart routing of payments for cost optimization
- Predictive maintenance of payment infrastructure
Regulatory Considerations
- MAS Compliance Strategy:
- Implement “explainable AI” approaches that satisfy MAS requirements
- Maintain detailed model risk management documentation
- Conduct regular bias testing to ensure fair outcomes
- Establish clear human oversight mechanisms for AI decisions
- Data Governance:
- Create comprehensive data management policies compliant with PDPA
- Implement data minimization and purpose limitation principles
- Ensure appropriate consent mechanisms for AI data processing
- Establish robust data security protocols
Competitive Differentiation Opportunities
- SME Banking Innovation:
- AI-powered cash flow forecasting for small businesses
- Automated invoice processing and payment recommendation
- Integration with accounting software for seamless payment operations
- Intelligent credit decision-making for faster financing
- Cross-Border Payment Enhancement:
- AI-driven optimization of international payment routing
- Real-time currency conversion rate optimization
- Enhanced compliance screening for international transactions
- Predictive analytics for foreign exchange management
Payment Fraud Landscape in Singapore:
- 49% of respondents have experienced payment fraud
- 33% of consumers feel less safe shopping compared to ten years ago
- 52% of businesses reported an increase in fraud attempts in the past year
Top Types of Payment Fraud in 2025:
- Phishing
- Social engineering attacks to steal personal information
- Increasingly sophisticated, using synthetic identities
- In 2024, victims lost S$59.4 million to phishing scams
- Refund Fraud / Policy Abuse
- Exploiting business return, refund, and promotion policies
- It can be conducted by professional fraudsters and every day consumers
- Experienced by nearly half of online merchants worldwide

- Card Testing
- Testing stolen cards to verify their active status
- Active cards can be sold at higher prices on the dark web
- Friendly Fraud / First-Party Fraud
- Consumers making purchases and then requesting chargebacks
- Accounts for up to 70% of credit card fraud
- Costs the industry over US$132 billion annually
Business Response to Fraud:
- 66% considering partnerships with providers offering chargeback liability guarantees
- 62% using AI to prevent fraudulent transactions
- 60% recognize fraud increases during peak shopping periods
Additional Payment Trends:
- 31% of Singaporeans don’t carry wallets
- 48% used mobile wallets in the past year
- QR code payments grew 31% year-on-year
- 51% shopped via social media platforms
The report highlights the growing sophistication of payment fraud and the need for robust security measures in Singapore’s digital payment ecosystem.

Payment Fraud Versions and Prevention Strategies:

- Phishing Characteristics:
- Sophisticated social engineering attacks
- Aim to steal Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
- Advanced tactics include creating synthetic identities
- In 2024, caused S$59.4 million in losses in Singapore
Prevention Methods:

- Implement robust second-factor authentication (2FA)
- Educate consumers about identifying suspicious communications
- Use AI-powered fraud detection systems
- Develop advanced identity verification technologies
- Regularly update security protocols to counter emerging tactics
- Refund Fraud / Policy Abuse Characteristics:

- Exploiting business return and refund policies
- Conducted by both professional fraudsters and opportunistic consumers
- Difficult to detect
- Affects nearly 50% of online merchants globally
Prevention Methods:

- Develop clear and strict refund policies.
- Implement sophisticated tracking systems for returns
- Use AI to identify suspicious return patterns
- Set reasonable time limits for returns
- Create detailed documentation requirements for refunds
- Monitor customer behaviour and flag unusual return activities
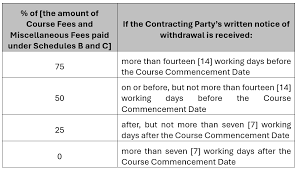
- Card Testing Characteristics:
- Fraudsters test stolen credit card details
- Aim to verify card validity
- Successful cards sold at higher prices on the dark web

Prevention Methods:
- Use advanced payment gateway fraud detection
- Implement real-time transaction monitoring
- Utilize machine learning algorithms to detect unusual transaction patterns
- Set up velocity checks to limit multiple quick transactions
- Use device fingerprinting technology
- Implement CAPTCHA and additional verification for suspicious transactions
- Friendly Fraud / First-Party Fraud Characteristics:

- Consumers make legitimate purchases, then request chargebacks
- Accounts for 70% of credit card fraud
- Costs the industry over US$132 billion annually
Prevention Methods:
- Maintain detailed transaction and delivery records
- Implement clear communication channels with customers
- Use chargeback management software
- Provide excellent customer service to resolve issues proactively
- Develop comprehensive documentation for each transaction
- Create transparent return and refund policies

Advanced Prevention Strategies:
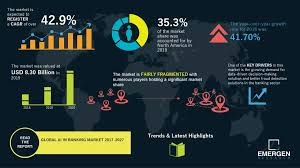
- Technology Integration
- 62% of businesses now use AI for fraud prevention
- Leverage machine learning and predictive analytics
- Implement real-time fraud detection systems
- Use blockchain for secure, transparent transactions

- Authentication Techniques
- Encourage second-factor authentication (2FA)
- Biometric verification
- Tokenization of payment information
- Continuous authentication during transactions

- Consumer Education
- Raise awareness about fraud tactics
- Provide guidelines for safe online shopping
- Encourage vigilance and reporting of suspicious activities

- Collaborative Approaches
- 66% of businesses considering partnerships with secure payment providers
- Share fraud intelligence across industries
- Develop cross-platform fraud detection networks
The evolving landscape of payment fraud requires a multi-layered, adaptive approach. Businesses must continuously update their prevention strategies, leverage advanced technologies, and maintain a proactive stance against emerging fraud tactics.

Maxthon
Maxthon has set out on an ambitious journey aimed at significantly bolstering the security of web applications, fueled by a resolute commitment to safeguarding users and their confidential data. At the heart of this initiative lies a collection of sophisticated encryption protocols, which act as a robust barrier for the information exchanged between individuals and various online services. Every interaction—be it the sharing of passwords or personal information—is protected within these encrypted channels, effectively preventing unauthorised access attempts from intruders.
Maxthon private browser for online privacyThis meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
In today’s rapidly changing digital environment, Maxthon’s unwavering commitment to ongoing security enhancement signifies not only its responsibility toward users but also its firm dedication to nurturing trust in online engagements. With each new update rolled out, users can navigate the web with peace of mind, assured that their information is continuously safeguarded against ever-emerging threats lurking in cyberspace.
