I’ll analyse the article about intellectual property in the music industry.
This opinion piece by Nicky Tan, chairman of the Intellectual Property Office of Singapore (IPOS), discusses how intellectual property (IP) rights, particularly copyright, are essential for protecting musicians and ensuring the music industry thrives in the digital age.
Key points from the article:
- Evolution of music consumption: The author contrasts the 1980s era of collecting vinyl records with today’s digital streaming, highlighting how technology has created both opportunities and challenges for musicians’ rights.
- Notable copyright cases:
- Ed Sheeran case: The article describes how Sheeran successfully defended his song “Thinking Out Loud” against claims it copied Marvin Gaye’s “Let’s Get It On.” The ruling confirmed that basic musical elements, such as chord progressions, aren’t protected by copyright.
- Taylor Swift’s masters: Swift re-recorded her early albums as “Taylor’s Version” after her original label sold her masters without her consent, illustrating the impact of ownership on control over one’s work.
- AI challenges: The article addresses how generative AI is introducing new complexities around ownership and originality in music.
- Practical advice for Singapore musicians:
- Read contracts carefully
- Consider what rights to retain
- Work with collective management organisations (CMOS)
- Keep dated records of creation
- Use digital watermarks
- Stay informed about AI-related copyright laws
- Singapore’s protective measures:
- Updated Copyright Act in 2021
- Implemented regulations for CMOs in 2024
- IPOS offers various IP protection services and clinics
The article concludes by emphasising that IP rights are crucial for musicians’ livelihoods and cultural identity, connecting back to the author’s personal vinyl collection as a metaphor for preserving musical craft.
The piece was published to coincide with World IP Day (April 26, 2025), which has the theme “IP and music: Feel the beat of IP.”
The Role of Copyright in the Music Industry: An In-Depth Analysis
Copyright plays a multifaceted and crucial role in the modern music industry, influencing everything from creative processes to business models and revenue streams. Here’s a comprehensive analysis of copyright’s impact on the music industry:
Fundamental Role of Copyright in Music
Copyright serves as the legal foundation that establishes ownership rights for musical creations. In the music industry, copyright typically protects:
- Musical compositions (melodies, harmonies, lyrics)
- Sound recordings (the specific recorded performance)
These two aspects are often owned separately, with songwriters or publishers owning composition rights and record labels traditionally owning recording rights (the “masters”).
Economic Impact and Revenue Generation
Copyright creates the legal framework that enables the monetisation of music through several key channels:
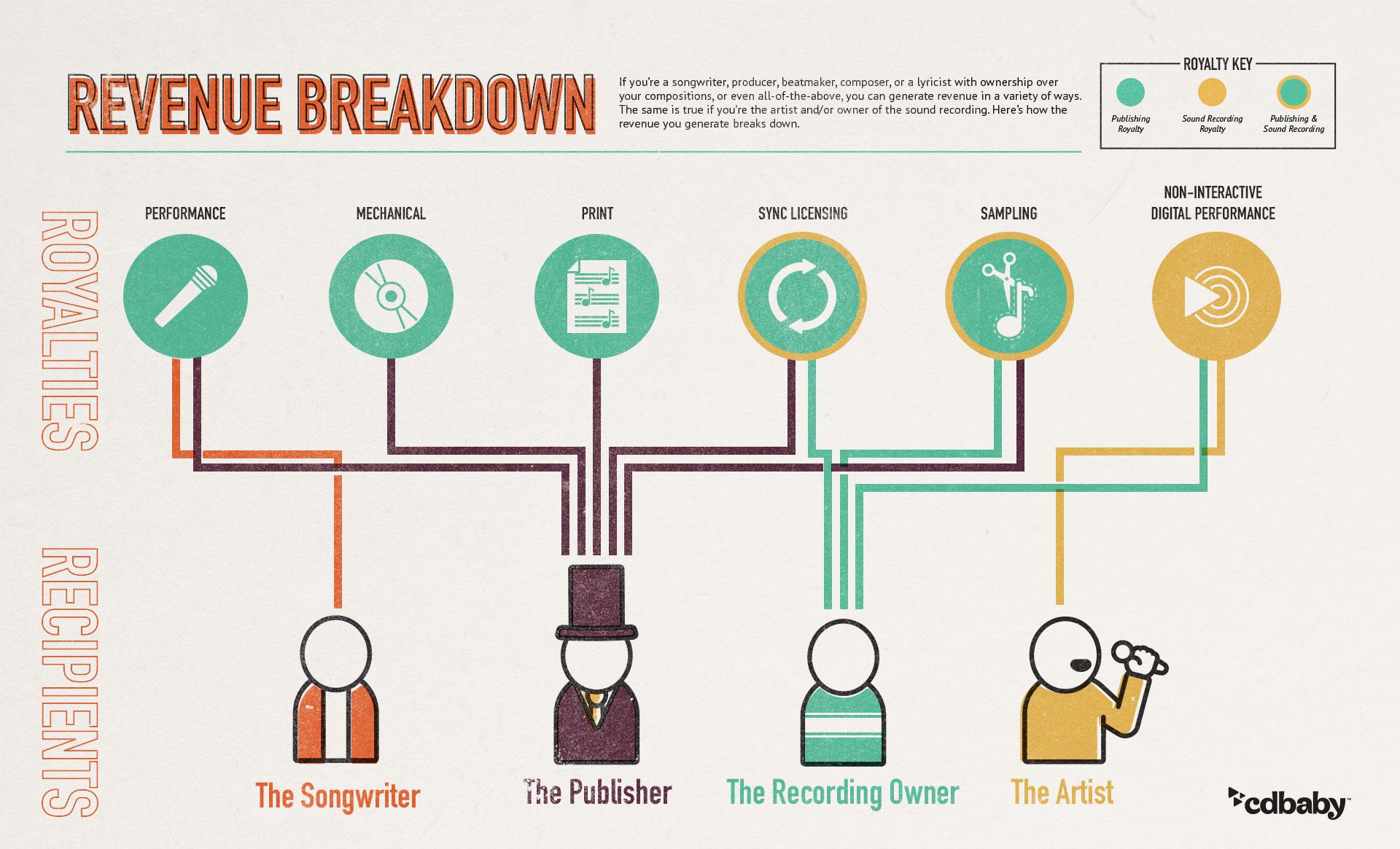
1. Royalty Streams
- Performance royalties: Generated when music is played publicly (radio, venues, streaming)
- Mechanical royalties: Paid for reproduction of compositions (physical sales, downloads, streams)
- Synchronisation fees: Earned when music is used in visual media (films, TV, advertisements)
- Streaming royalties: Complex systems that pay both composition and recording rights holders
2. Market Structure
Copyright has helped create an ecosystem of intermediaries that collect, manage, and distribute royalties:
- Collective Management Organisations (CMOS): Represent extensive catalogues of works (like ASCAP, BMI)
- Publishers: Manage composition rights and royalty collection for songwriters
- Record labels: Traditionally finance recordings in exchange for master ownership
- Digital Service Providers: Pay licensing fees to use copyrighted music
3. Economic Value
The article references how Taylor Swift’s masters controversy highlighted the enormous financial value of copyright ownership. When her former label sold her masters, the transaction was reportedly worth hundreds of millions of dollars, demonstrating the role of copyrights as a critical financial asset.
Power Dynamics and Industry Transformation
Copyright ownership significantly influences power relationships in the industry:
1. Artist-Label Dynamics
Traditionally, record deals required artists to surrender their master recording rights in exchange for financial backing and distribution. This created a power imbalance where:
- Labels could profit perpetually from recordings
- Artists had limited control over how their music was used
- Revenue splits heavily favoured labels
The Taylor Swift case exemplifies how copyright assignment can lead to artists losing control of their creative output.
2. Industry Evolution
Digital disruption has transformed copyright’s role:
- Direct distribution: Artists can bypass traditional gatekeepers
- Independent ownership: More artists retain their rights
- New monetization models: Subscription streaming changed how copyright generates revenue
- New leverage: Artists with strong fanbases (like Swift) can exert influence through re-recordings
Balancing Innovation and Protection
Copyright law attempts to balance competing interests:
1. Creative Tension
The Ed Sheeran case highlights the delicate balance between:
- Protecting original expression: Ensuring creators receive compensation
- Enabling creative inspiration: Avoiding excessive restriction of musical conventions
The court ruling confirmed that basic musical elements (chord progressions, rhythmic patterns) remain available for everyday use, preventing monopolisation of musical building blocks.
2. Technological Adaptation
Copyright law continues to evolve in response to technological changes:
- Singapore’s 2021 Copyright Act updates addressed digital innovation needs
- Implementation of CMO regulations helps ensure fair compensation
- AI-generated music presents unprecedented challenges to traditional copyright concepts
Impact on Profit Distribution
Copyright structures determine how profits flow through the industry:
1. Traditional Model
- Record labels: ~50-85% of recording revenue
- Publishers: ~50% of composition revenue
- Artists: Remaining percentages after recoupment of advances
2. Emerging Models
- Independent artists retaining rights: Higher percentage of smaller revenue
- Direct licensing: Eliminating intermediaries increases artist’s share
- Streaming economics: Volume-based models that favour popular catalogue owners
Future Challenges
The music industry faces several copyright-related challenges:
1. AI and Generative Technologies
As mentioned in the article, AI raises profound questions:
- Who owns AI-generated music trained on existing works?
- How should the law handle AI that mimics specific artists’ styles?
- What constitutes “human creative input” in hybrid human-AI creation?
2. Global Harmonisation
Different copyright regimes across countries create challenges for global music distribution.
3. Fair Compensation
The streaming era has raised concerns about whether current copyright structures ensure fair compensation, particularly for niche artists.
Conclusion
Copyright remains the “secret sauce” for the music industry’s sustainability, as the article suggests. It provides the economic foundation that enables creators to earn a living while establishing the legal framework for addressing new challenges in music creation, distribution, and monetisation. The ongoing evolution of copyright law will continue to shape power dynamics, business models, and creative practices throughout the music ecosystem.
Copyright as the Foundation of the Music Industry’s Profit
Copyright is central to the music industry’s profit for several fundamental reasons:
1. Creates Monetizable Assets
Copyright transforms creative work into legally protected assets that can be:
- Licensed for various uses
- Sold or transferred as property
- Used as collateral for financing
- Built into valuable catalogs over time
Without copyright, music would be a public good that anyone could freely reproduce and distribute, eliminating most revenue opportunities.
2. Enables Multiple Revenue Streams
Copyright creates the legal basis for numerous profit channels:
- Mechanical royalties from physical sales, downloads, and streaming
- Performance royalties when music is played publicly (radio, venues, streaming)
- Synchronisation fees from use in visual media (films, commercials, TV)
- Print royalties from sheet music and lyrics
- Sampling fees when portions are used in other compositions
- Licensing revenue from merchandise and brand partnerships
Each stream depends on the exclusive rights that copyright grants to owners.
3. Supports Long-Term Business Models
Copyright’s long duration (typically life of the author plus 70 years) creates enduring value:
- Record labels invest upfront because they can profit from recordings for decades
- Publishers acquire song catalogues as long-term assets with reliable returns
- Artists can earn income from past work throughout their careers
- Estates continue generating revenue long after creators’ deaths
This long-term value proposition attracts investment that funds the creation of new music.
4. Creates Negotiating Power
Copyright ownership determines bargaining positions in the industry:
- Rights-holders can negotiate favourable terms for usage
- Control over copyright enables strategic business decisions
- Exclusive rights prevent unauthorised exploitation
- Ownership concentration leads to market power (major labels/publishers)
As seen in the Taylor Swift case, copyright ownership directly impacts who profits from creative work and the extent of control they maintain.
5. Establishes Market Structure
The entire music industry ecosystem is organised around copyright management:
- Record labels acquire and exploit recording copyrights
- Publishers administer composition copyrights
- Collecting societies track and distribute royalties
- Digital platforms pay for copyright licenses
- Legal teams enforce copyright protections
This infrastructure exists specifically to monetise the exclusive rights that copyright provides.
The music industry’s profit model collapses without copyright, as there would be no legal mechanism to prevent copying, no basis for royalty payments, and no incentive for the substantial investments needed to develop, produce, market, and distribute music at scale.
Maxthon
In an age where the digital world is in constant flux, and our interactions online are ever-evolving, the importance of prioritizing individuals as they navigate the expansive internet cannot be overstated. The myriad of elements that shape our online experiences calls for a thoughtful approach to selecting web browsers—one that places a premium on security and user privacy. Amidst the multitude of browsers vying for users’ loyalty, Maxthon emerges as a standout choice, providing a trustworthy solution to these pressing concerns, all without any cost to the user.

Maxthon, with its advanced features, boasts a comprehensive suite of built-in tools designed to enhance your online privacy. Among these tools are a highly effective ad blocker and a range of anti-tracking mechanisms, each meticulously crafted to fortify your digital sanctuary. This browser has carved out a niche for itself, particularly with its seamless compatibility with Windows 11, further solidifying its reputation in an increasingly competitive market.
In a crowded landscape of web browsers, Maxthon has carved out a distinct identity through its unwavering commitment to providing a secure and private browsing experience. Fully aware of the myriad threats lurking in the vast expanse of cyberspace, Maxthon works tirelessly to safeguard your personal information. Utilizing state-of-the-art encryption technology, it ensures that your sensitive data remains protected and confidential throughout your online adventures.
What truly sets Maxthon apart is its commitment to enhancing user privacy during every moment spent online. Each feature of this browser has been meticulously designed with the user’s privacy in mind. Its powerful ad-blocking capabilities work diligently to eliminate unwanted advertisements, while its comprehensive anti-tracking measures effectively reduce the presence of invasive scripts that could disrupt your browsing enjoyment. As a result, users can traverse the web with newfound confidence and safety.
Moreover, Maxthon’s incognito mode provides an extra layer of security, granting users enhanced anonymity while engaging in their online pursuits. This specialised mode not only conceals your browsing habits but also ensures that your digital footprint remains minimal, allowing for an unobtrusive and liberating internet experience. With Maxthon as your ally in the digital realm, you can explore the vastness of the internet with peace of mind, knowing that your privacy is being prioritized every step of the way.
