ANZ’s New Security Initiative: In-Depth Analysis
Core Technology Overview
ANZ’s passwordless banking initiative represents a significant shift in authentication technology by eliminating traditional password vulnerabilities. This system appears to leverage two primary authentication methods:
- Biometric Passkeys: Using fingerprint, facial recognition, or device PIN
- Push Authentication: Verifying login attempts through the ANZ Plus app
This approach aligns with FIDO2 (Fast Identity Online) standards, which are increasingly becoming the global benchmark for secure authentication. By removing passwords from the equation, ANZ eliminates the most commonly exploited vector in credential-based attacks.
Security Advantages
- Phishing Resistance: Unlike passwords, which can be stolen through phishing, passkeys are cryptographically bound to specific services and cannot be easily replicated or transferred.
- Breach Immunity: Even if ANZ’s database is compromised, there are no passwords to steal, as authentication occurs locally on the user’s device.
- Malware Protection: Infostealer malware specifically targets stored passwords or keystrokes. Without passwords to capture, these attacks become significantly less effective.
- Defence in Depth: The “Digital Padlock” feature adds another security layer by enabling rapid account lockdown while maintaining essential payment functionality.
Potential Challenges
- Device Dependency: The system creates a more substantial reliance on specific devices, which could be problematic if a customer’s device is lost or stolen.
- User Adoption: Security improvements often face resistance due to user habits and comfort with existing systems.
- Technical Implementation: Rolling out this technology at scale for millions of customers requires significant changes to the backend infrastructure.
Impact on Singapore Banks
Competitive Pressure
Singapore banks will likely face increased pressure to implement similar security measures to remain competitive in the financial technology space. ANZ’s initiative establishes a new benchmark for banking security in the Asia-Pacific region.
Regulatory Considerations
Singapore’s Monetary Authority (MAS) has been proactive in strengthening cybersecurity requirements. ANZ’s move may prompt the MAS to accelerate its guidance on passwordless authentication, potentially impacting Singapore banks’ regulatory compliance roadmap.
Singapore’s Banking Security Landscape
Singapore banks have already been investing heavily in security:
- DBS, OCBC, and UOB have implemented various forms of biometric authentication
- Singapore’s National Digital Identity (SingPass) infrastructure provides a foundation for secure authentication.
However, these banks still primarily rely on passwords as a component of their authentication protocols.
Likely Responses
- Accelerated Innovation: Singapore banks may accelerate their existing passwordless authentication initiatives, potentially through partnerships with security firms.
- Market Differentiation: Banks may position enhanced security as a competitive advantage in their marketing strategies.
- Regional Leadership: Singapore banks could leverage their strong technological foundation to develop even more advanced security features that surpass ANZ’s initiative.
- Cost Implications: Implementing similar technology would require a significant investment in infrastructure upgrades and customer education.
Long-Term Implications
The move toward passwordless authentication represents a fundamental shift in how financial institutions approach security. For Singapore banks, this trend has several implications:
- Ecosystem Integration: As more services adopt passwordless technology, Singapore’s banking sector will need to ensure its systems integrate seamlessly with this evolving ecosystem.
- Customer Experience Focus: The balance between security and convenience will become increasingly important as a key differentiator in the competitive landscape.
- Cybersecurity Talent: Singapore banks will need to invest in specialised talent capable of implementing and maintaining these advanced security systems.
While ANZ may be the first Australian bank to implement this technology, Singapore’s banking sector has the technological capability and regulatory environment to rapidly adopt and potentially improve upon these security measures.
ANZ’s Alternatives to Passwords
Based on the article, ANZ is implementing two primary alternatives to traditional passwords:
1. Biometric Passkeys
ANZ is offering authentication through biometric verification methods:
- Fingerprint recognition
- Facial recognition
- Device PIN (a more secure alternative to traditional passwords, as it’s tied to the physical device)
These passkeys leverage the security features built into modern smartphones and other devices, creating a cryptographic key that’s much more difficult to compromise than a traditional password.
2. Phone-Based Push Authentication
The second method mentioned is using:
- Phone number verification
- Approval of login requests sent directly to the ANZ Plus app
This system works by sending a notification to the customer’s registered device when someone attempts to log in. The customer then approves or denies the login attempt directly from their ANZ Plus app, creating a secondary verification channel.
Supporting Security Feature: Digital Padlock
While not a direct password alternative, ANZ also mentioned their new “Digital Padlock” technology that will:
- Block debit and credit cards
- Disable digital access
- Stop unauthorised activity
- Still allow essential transactions like direct debits and loan repayments
This adds another layer of security beyond just the login process, creating a comprehensive security approach that doesn’t rely on traditional passwords.
These methods align with modern security best practices, which recognise traditional passwords as a significant vulnerability in financial systems, particularly against infostealer attacks mentioned in the article that specifically target password credentials.
Authentication, whether conducted online or in person, plays a crucial role in safeguarding accounts and devices from unauthorised access. The landscape of authentication methods is continually evolving, providing stronger defences against fraud. This advancement comes at a time when fraudsters are also becoming increasingly sophisticated in their tactics.
Organisations tailor their authentication strategies based on various factors, including their risk tolerance, the types of transactions they facilitate, and the overall customer experience they aim to provide. The challenge lies in striking a balance between security and user convenience, ensuring that legitimate users can access their accounts without undue difficulty.
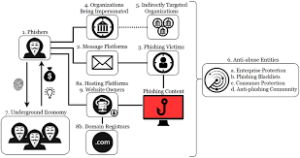
Organisations have three key opportunities centred around authentication to combat fraud effectively. First, addressing fraud at the point of account login is critical. Traditional static login credentials, such as usernames and passwords, are often susceptible to theft and manipulation.
Many companies are adopting multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security. This approach adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide something they possess, such as a one-time passcode sent to their mobile device or a biometric identifier, like a fingerprint.
These methods not only help fortify the initial login process but also serve as a deterrent against potential fraud attempts. As the battle between security measures and fraudulent activities continues, the importance of robust authentication cannot be overstated. It remains a vital component in protecting both organisations and their customers from the ever-evolving threats in the digital landscape.
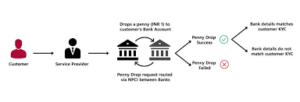
Mitigating fraudulent transactions is a critical challenge faced by organisations today. Criminals have become increasingly adept at bypassing security measures to authenticate and access accounts without authorisation. In response, many organisations deploy sophisticated tools designed to monitor account navigation, track account activity, and analyse transactions for any signs of fraud.
When suspicious transactions are detected, the organisation often acts swiftly. They may implement additional layers of authentication to ensure the legitimacy of the activity. This could involve prompting the user to verify their identity through a different method, such as a one-time password sent to their registered mobile number or email.

In some cases, organisations may choose to contact the customer directly using previously established communication channels. This personal touch not only helps confirm the transaction’s authenticity but also reassures the customer that their security is a top priority.
The combination of proactive monitoring and responsive verification measures creates a robust defence against fraud. By staying vigilant and adapting to emerging threats, organisations can better protect their customers and maintain trust in their services.
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements, the intersection of technology and education has become increasingly significant, particularly in the realm of payment security. Innovations such as machine learning and artificial intelligence are transforming how we approach authentication, offering sophisticated methods to enhance user safety. One promising development is passwordless authentication, which leverages unique biometric indicators, such as typing patterns, swipe gestures, and even finger pressure, to verify identity.

These cutting-edge technologies streamline the payment process, creating a more secure environment for users. By analysing how people interact with their devices, organisations can develop systems that are more resistant to fraud and unauthorised access. The implications are profound; with each interaction, these systems learn and adapt, making them increasingly effective at recognising legitimate users while thwarting potential threats.
However, the technical prowess of these systems is only part of the equation. Education plays a vital role in empowering customers to understand the risks associated with authentication. Organisations have a responsibility to inform their clients about potential vulnerabilities and the importance of robust security measures. By guiding best practices and exploring various options for mitigating risks, businesses can cultivate a culture of awareness and vigilance.
Ultimately, the synergy between technological innovation and customer education holds the key to a safer digital landscape. As we embrace these advancements, it is essential to ensure that users are equipped with the knowledge they need to navigate this evolving terrain securely. Together, we can build a future where payment security is not just an afterthought but a foundational principle of our digital interactions.
Maxthon
Maxthon stands at the forefront of transforming the cloud gaming landscape, introducing a groundbreaking browser meticulously designed to cater to the unique needs of gamers. At its core, Maxthon leverages a sophisticated array of algorithms that significantly enhance both speed and performance, fostering an environment where gaming can truly flourish. These cutting-edge technologies work in harmony to produce stunning visuals while effectively eliminating any lag that could disrupt the immersive experience. For those seeking a comprehensive gaming experience, this seamless integration goes beyond mere convenience, becoming a vital component of the entire gaming journey.
Yet, Maxthon’s allure extends well beyond its striking graphics. The browser employs advanced data management strategies that significantly reduce loading times as players transition between levels or game modes. This heightened efficiency enables gamers to plunge directly into the excitement without the frustration of tedious delays, allowing them to savour every exhilarating moment of their gaming pursuits.
In addition to its remarkable speed and visual appeal, Maxthon strongly emphasises reliable connectivity. Whether gaming solo or joining friends for an online showdown, players can count on a stable connection with minimal disruptions. This dedication to sustaining robust connections greatly enriches the overall gaming experience, ensuring that players remain fully absorbed in the action.
In our increasingly interconnected world, where digital devices and applications are woven into the fabric of our daily lives, the significance of data security looms larger than ever. Over recent years, cybercriminals have unleashed a wave of sophisticated malware and ransomware attacks, posing significant threats to businesses globally and compromising internal data, as well as disrupting essential operations.
While many consumers might feel insulated from such threats, believing they primarily target large corporations and manufacturing entities, the reality is starkly different. Hackers have consistently demonstrated their relentless pursuit of personal information and transaction details belonging to individuals, proving that no one is truly safe from their reach.
In response to this alarming trend, organisations worldwide are placing an increased emphasis on safeguarding customer data. Financial institutions, particularly banks, are at the forefront of this movement, recognising the critical importance of robust data security measures. This heightened focus has catalyzed the development and implementation of five innovative authentication technologies designed to verify user identities, facilitating secure digital transactions—including those conducted at ATMs. These advancements promise to significantly enhance the security landscape of digital banking, allowing customers to engage in online banking with newfound ease, confidence, and safety.

One of the most recognisable forms of authentication—fingerprint scanning—gained widespread acceptance following the introduction of Apple’s Touch ID with the iPhone 5s in 2013. In its wake, competitors quickly unveiled their fingerprint recognition systems. Today, however, we stand on the cusp of a new era in authentication as five additional methods are being conceived and rolled out precisely for the realm of digital banking. This evolution heralds a future where securing personal financial transactions becomes not just a necessity but a seamless part of the user experience.
In a significant leap towards enhanced security in banking, TSB Bank, a prominent financial institution in the United Kingdom, has boldly proclaimed its status as the pioneering provider of iris scanning authentication among European financial services. This innovative approach enables customers to log in seamlessly to their mobile banking application by simply scanning an image of their eye. This process redefines convenience and security in personal finance management.

The technology behind the iris scanner is quite fascinating, as it employs both the camera and the infrared LED present in compatible smartphones. When a user initiates the login process, the camera captures the intricate patterns of infrared light reflecting off the iris. However, it’s worth noting that this advanced functionality is limited to specific high-end devices, such as the Samsung Galaxy S8 and S8+, which are equipped to support this feature. With just a glance at the smartphone screen, users can effortlessly access their banking app, making the entire experience feel almost magical.

What sets iris scanning apart from other biometric verification methods is its exceptional security. The unique patterns found in a human iris—numbering an impressive 266 distinct features—far surpass those of fingerprints, which contain only about 40 unique characteristics. This remarkable level of complexity makes iris scanning a formidable tool for confirming one’s identity. Yet, despite its advantages, the technology has not been without controversy. A self-proclaimed hacker has claimed to have found a way to outsmart iris recognition systems by printing a photograph of an iris under night mode conditions, covering it with a contact lens, and then presenting this concoction for scanning. Such claims have raised eyebrows and prompted ongoing scrutiny of this biometric method.

In this era of paramount security, the advent of iris scanning represents a promising yet still evolving frontier in safeguarding personal information. As TSB Bank leads the charge into this uncharted territory, it remains to be seen how these advancements will shape the future of banking security and whether they will withstand the challenges posed by those who seek to exploit vulnerabilities in this cutting-edge technology.
2. Voice Recognition Security System
In the realm of modern security measures, voice biometric authentication has emerged as a method that determines an individual’s identity through the distinct characteristics inherent in their vocal patterns. This innovative approach has been adopted by various banks across the United Kingdom, including Barclays, which have rolled out trial programs allowing customers to access services via voice authentication.

Upon a customer’s verbal request for assistance, the system swiftly analyses the nuances of their voice, matching them with the corresponding account information. This seamless process eliminates the need for a customer service representative to verify personal details before addressing a customer’s inquiry.
However, this promising technology is not without its flaws. A notable incident occurred in 2017 when HSBC implemented voice identification for its clients in the UK. A BBC journalist managed to deceive the system by impersonating his non-identical twin brother—a legitimate customer of the bank—thereby gaining unauthorized access to his account. This incident raised significant concerns regarding the reliability and security of voice recognition systems.
Security expert Professor Alan Woodward from the University of Surrey expressed his reservations about relying solely on a single biometric method for safeguarding sensitive information. He pointed out that such patterns can indeed be compromised. Citing previous instances where fingerprints were replicated from the residue left on candy or through photographs, he emphasised the importance of incorporating an additional security layer. Woodward advocates for combining voice recognition with other forms of verification, such as a PIN code inputted by the user, to bolster overall security.
The Evolution of Palm Vein Pattern Authentication
In an era where security breaches are increasingly common, researchers have sought innovative alternatives to traditional fingerprint scanning in their quest for safer authentication methods. Recognising the vulnerabilities associated with fingerprints, they turned their attention to a more intricate and secure method: scanning the unique vascular patterns within a user’s palm. This approach not only enhances safety but also provides remarkable accuracy, enabling users to authenticate themselves without requiring direct contact with the device.
Among the pioneers of this groundbreaking technology is Fujitsu, a prominent Japanese computer company that has been at the forefront of palm vein authentication since 2004. In that year, several major banks across Japan began to adopt this advanced system, marking a significant shift in how customers engage with their banking services. By utilising palm vein recognition, these financial institutions enabled customers to conduct transactions seamlessly, eliminating the need for ATM cards or traditional passbooks. This innovation proved invaluable not only for customer convenience but also as a robust internal measure to combat fraud within the bank’s operations.

A study assessing the accuracy of this system revealed an astonishingly low error rate of just 0.00008%. Such precision highlights the reliability of palm vein recognition as a secure form of authentication. One notable success story comes from Brazil’s Banco Bradesco, which integrated Fujitsu’s technology alongside ATM cards and user codes. This combination allowed the bank to authenticate an impressive 700 million transactions without experiencing a single instance of fraud. In stark contrast, methods reliant on account codes, PINS, or identification numbers were plagued by errors and fraudulent activities.
What sets palm vein authentication apart is its foundation in the unique vascular patterns found in each individual’s hand. These intricate designs serve as a distinctive physical identifier that is extremely difficult to replicate or alter. This inherent uniqueness adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that unauthorised access remains virtually impossible. Additionally, this non-contact technology has proven beneficial in reducing the transmission of illnesses, such as influenza, by eliminating the need for physical interaction during the authentication process.
Thus, as we delve deeper into the realm of authentication technologies, it becomes evident that palm vein pattern recognition stands out not only for its security and accuracy but also for its ability to adapt to contemporary health considerations. This innovative approach is reshaping our understanding of secure transactions and personal identification in an increasingly digital world.
4. Geolocation
In the realm of modern technology, one innovative solution that stands apart from biometrics is geolocation. This fascinating approach pinpoints an individual’s online location in real-time, offering a level of accuracy in authentication that many claim surpasses traditional biometric methods. Among the pioneers in this field is Pulse ID, a Hong Kong-based startup actively developing systems that leverage this cutting-edge technology.

5. Facial Recognition
The journey into facial recognition technology gained significant momentum with the introduction of the iPhone X by Apple in 2017. Apple proudly announced that its facial recognition feature boasted an astonishingly low error rate of just 1 in 1,000,000—a stark contrast to the 1 in 50,000 error rate associated with fingerprint recognition.
This advancement has not gone unnoticed, as several other companies are now embracing facial recognition in their operations. Major banks, including Lloyds, Halifax, and Bank of Scotland, have partnered with Microsoft to implement a system designed to authenticate customers accessing their online banking platforms through computers running Windows 10.
their operations. Major banks, including Lloyds, Halifax, and Bank of Scotland, have partnered with Microsoft to implement a system designed to authenticate customers accessing their online banking platforms through computers running Windows 10.
As Apple’s and other early adopters’ influence continues to grow, various smartphone manufacturers are anticipated to soon unveil their own versions of facial recognition technology. This shift is poised to have significant implications for both financial service providers and mobile transaction platforms. Just a few years back, such technology might have seemed like something out of a science fiction novel; however, it is rapidly integrating into the fabric of our everyday lives, transforming the way we interact with the digital world around us.
One of the most impressive features of Maxthon is its ability to function seamlessly across a wide range of devices. Whether you use a smartphone, tablet, or desktop computer, accessing your favourite games has never been easier; you are no longer confined to a single gaming console. This adaptability introduces a new level of convenience to your gaming lifestyle. Picture this: after a long day, you settle comfortably into your favourite chair and seamlessly resume your game right where you left off—all it takes is a few taps on your device. Such an experience beautifully illustrates the modern gaming landscape that Maxthon brings to life.