Backbase has announced what they’re calling the “world’s first AI-powered Banking Platform” on April 29, 2025. This platform represents a significant evolution in banking technology with several notable features:
Core Capabilities
- Unifies two critical domains: customer servicing and digital sales
- Powered by their “Intelligence Fabric” (initially launched in September 2024)
- Incorporates “Agentic AI” – modular, intelligent agents designed explicitly for banking operations
Key Benefits for Banks
- AI-powered self-service and real-time customer support
- AI integration into daily operations to enhance employee productivity
- Streamlined and automated sales processes
- AI-driven cross-selling to deepen customer relationships
Strategic Context
- Positions traditional banks to compete against fintech disruptors
- Addresses the challenge of legacy tech and fragmented data in banking
- Aims to help banks move from basic digital channels to “AI-powered growth orchestration”
- Focuses on customer acquisition, activation, expansion, and retention at scale
Implementation Support
- Includes the “AI Factory” – an embedded delivery model to bridge AI skills gaps
- Provides AI experts to work directly with banks’ teams
- Designed for rapid deployment without extensive experimentation
The platform is described as “production-ready” and “globally available” as of the date of the press release, with early adopters already experiencing benefits in efficiency and growth.
In-Depth Analysis: Backbase’s AI-Powered Banking Platform and Its Implications
Comprehensive Analysis of Backbase’s AI-Powered Banking Platform
Backbase’s newly launched AI-powered Banking Platform represents a significant evolution in banking technology infrastructure. Let’s analyse this development in depth:
Core Technology Components
- Intelligence Fabric Foundation
- Serves as the unified data foundation
- Integrates behavioural signals, transactional data, and operational insights
- Converts disparate data into real-time, actionable intelligence
- First introduced in September 2024, now fully integrated into the platform
- Agentic AI Architecture
- Employs modular, purpose-built AI agents specifically for banking functions
- Operates within defined guardrails for safety and compliance
- Embeds into existing service and sales journeys
- Automates routine tasks while guiding next-best actions
- Unified Sales and Servicing Approach
- Breaks down traditional silos between customer service and sales functions
- Creates a continuous engagement loop from service to sales opportunities
- Enables contextual, AI-driven recommendations during customer interactions
Strategic Banking Transformation
The platform addresses several critical challenges in modern banking:
- Passive to Proactive Banking Model
- Shifts from reactive customer service to proactive engagement
- Uses predictive analytics to anticipate customer needs
- Transforms service touchpoints into growth opportunities
- Operational Efficiency
- Automates routine tasks across front and back-office operations
- Reduces manual processing and administrative overhead
- Potentially significant cost savings through streamlined operations
- Revenue Generation
- Enhances cross-selling and upselling through AI-driven recommendations
- Identifies optimal timing for product offerings based on customer behaviours
- Personalises offerings at scale across the customer base
Impact on Singapore Banks
Singapore’s banking sector is particularly well-positioned to benefit from this technology for several reasons:
Alignment with Singapore’s Smart Nation Initiative
Backbase’s AI platform aligns with Singapore’s national digital transformation strategy, which emphasises advanced technology adoption in financial services. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has been actively promoting the adoption of AI in financial services through its AI and Data Analytics (AIDA) Grant and related programs.
Competitive Landscape Considerations
- Local Banks (DBS, OCBC, UOB)
- These banks have already invested heavily in digital transformation
- DBS has particularly positioned itself as a digital leader
- Backbase’s platform could help accelerate their AI capabilities while reducing the need for in-house development
- Likely to focus on integration with existing digital ecosystems
- Foreign Banks Operating in Singapore
- May use this technology to compete more effectively with local incumbents
- Could leverage the platform to quickly scale operations without a significant physical footprint
- Potential advantage in wealth management services through AI-driven personalisation
- Digital Banks (Trust Bank, GXS, Maribank)
- New digital-only banks can utilise this platform to rapidly scale their capabilities.
- It may help bridge the experience gap with established players
- Potential for more efficient operations given their leaner structures
Regulatory Considerations
Singapore’s regulatory framework is conducive to AI adoption while maintaining strong governance:
- MAS has established clear AI governance frameworks
- The platform’s built-in compliance features align with Singapore’s emphasis on responsible AI use
- The “transparent, secure, and auditable” design claims would appeal to MAS requirements
Mitigating Tariff Crisis Impacts
While the press release doesn’t explicitly mention tariff crises, Backbase’s platform offers several capabilities that could help banks navigate economic disruptions caused by trade tensions:
Real-Time Risk Assessment
- Dynamic Portfolio Analysis
- The Intelligence Fabric could potentially analyse corporate and commercial portfolios in real-time.
- Identify exposures to industries affected by tariff changes
- Enable proactive portfolio adjustments before impacts materialise
- Supply Chain Financing Optimisation
- AI-powered analysis of supply chain dependencies
- Identification of alternative financing solutions for affected businesses
- Prediction of cash flow impacts from tariff-related disruptions
Customer Support During Economic Uncertainty
- Personalised Financial Guidance
- AI agents could provide tailored advice to customers affected by economic disruption.
- Scale personalised support across large customer bases during crisis periods.
- Deliver consistent, compliant guidance on complex financial matters
- Early Intervention Programs
- Identify customers and businesses at risk from tariff impacts
- Proactively offer restructuring or support options
- Reduce default rates through early engagement
Operational Resilience
- Scenario Planning and Stress Testing
- The platform’s predictive capabilities could support advanced scenario planning
- Model potential impacts of various tariff scenarios
- Support capital allocation decisions in volatile environments
- Resource Optimization
- During crisis periods, AI automation could free up human resources for higher-value activities
- Enable more efficient allocation of expertise to complex cases
- Maintain service levels despite increased customer inquiries during uncertainty
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
Despite the potential benefits, Singapore banks would face several challenges in implementing this technology:
- Integration with Legacy Systems
- Requires careful planning to connect with existing infrastructure
- Data migration and quality issues must be addressed
- Potential need for phased implementation approach
- Talent and Capability Development
- The “AI Factory” component acknowledges the skills gap challenge
- Banks would need to develop internal capabilities to maximise platform benefits
- Cultural adaptation to AI-augmented workflows
- ROI Timeline and Measurement
- Substantial investment required for full implementation
- Benefits may take time to materialise across all areas
- Need for clear KPIS to track impact on efficiency and growth
Conclusion
Backbase’s AI-powered Banking Platform represents a significant advancement in banking technology that aligns well with Singapore’s digital banking ambitions. While not explicitly designed for tariff crisis management, its capabilities in data integration, predictive analytics, and customer engagement could provide valuable tools for navigating economic uncertainty. The platform’s success in Singapore will likely depend on how effectively it can be integrated with existing systems and how well banks can develop the necessary capabilities to leverage its full potential.
In-Depth Analysis of Backbase’s AI Banking Platform Core Features
Data Integration Capabilities
Backbase’s “Intelligence Fabric” forms the foundation of their AI-powered Banking Platform’s data integration approach. Let’s analyze this component in depth:
Architecture and Technical Framework
- Unified Data Foundation
- Appears to function as a data mesh or data fabric architecture
- Likely incorporates both batch and real-time data processing pipelines
- Creates a single source of truth across previously siloed banking systems
- Addresses the fragmentation challenge common in banking infrastructures
- Data Sources Integration
- Customer Behavioral Data: Captures digital interactions, channel preferences, and engagement patterns
- Transactional Data: Processes payment flows, account activities, and financial movements
- Operational Data: Incorporates workflow metrics, service interactions, and process efficiency data
- External Data: May include market indicators, economic signals, and competitive intelligence
- Data Orchestration
- Harmonises data from multiple banking systems with different schemas and structures
- Likely employs advanced ETL/ELT processes with semantic data mapping
- Establishes consistent customer identities across product lines and channels
- Creates temporal continuity in customer journeys across touchpoints
- Real-Time Processing Capabilities
- Enables stream processing of transactional and interaction data
- Supports event-driven architecture for immediate response to customer actions
- Reduces data latency for time-sensitive decisions and interventions
- Facilitates continuous customer journey monitoring and optimisation
Differentiation and Innovation
The Intelligence Fabric differs from traditional banking data warehouses in several ways:
- Contextual Intelligence
- Enriches raw data with situational context (location, device, time, previous interactions)
- Establishes meaningful connections between seemingly unrelated data points
- Constructs a multi-dimensional view of customer relationships beyond transactions
- Activation-Ready Data
- Transforms insights into immediately actionable formats for front-line systems
- Provides pre-processed data structures optimized for AI agent consumption
- Enables “last-mile” data delivery to customer-facing applications
Predictive Analytics Capabilities
Backbase’s platform incorporates sophisticated predictive analytics that extend beyond traditional banking analytics approaches:
Core Analytical Functions
- Customer Behavioral Modeling
- Develops probabilistic models of future customer actions based on patterns
- Likely employs machine learning techniques including:
- Classification models for propensity scoring
- Sequence modeling for journey prediction
- Anomaly detection for unusual patterns
- Reinforcement learning for optimizing interventions
- Financial Pattern Recognition
- Identifies spending patterns and financial behaviors indicative of life events
- Detects early signals of changing financial circumstances
- Recognizes transaction clusters suggesting new financial needs
- Forecasts cash flow patterns and liquidity requirements
- Next-Best-Action Intelligence
- Evaluates potential interventions across multiple dimensions:
- Likelihood of customer acceptance
- Short and long-term profitability
- Risk implications
- Operational feasibility
- Continuously updates recommendations based on new data
- Evaluates potential interventions across multiple dimensions:
- Prescriptive Analytics
- Moves beyond prediction to recommend specific actions
- Incorporates business constraints and objectives into recommendations
- Suggests optimal timing, channel, and messaging for interventions
- Supports A/B testing and experimental design to refine recommendations
Advanced Features
- Causal Inference Capabilities
- Likely incorporates causal modeling beyond correlation analysis
- Enables understanding of intervention effects rather than just associations
- Supports counterfactual analysis (“what if” scenarios)
- Explainable AI Framework
- Provides transparency into AI decision factors
- Supports regulatory compliance regarding automated decisions
- Enables banker understanding of AI recommendations
- Facilitates human-AI collaboration in complex decisions
- Continuous Learning
- Implements feedback loops from interventions to model refinement
- Adapts to evolving customer behaviors and market conditions
- Reduces model drift through ongoing validation and calibration
Customer Engagement Features
The platform’s customer engagement capabilities represent a significant evolution in banking engagement models:
Engagement Framework Components
- AI-Powered Self-Service
- Conversational Interfaces: Likely includes natural language understanding for customer inquiries
- Proactive Guidance: Anticipates customer needs before explicit requests
- Contextual Assistance: Provides help based on current customer situation
- Journey Continuation: Enables seamless transitions between channels and sessions
- Real-Time Support Systems
- Intelligent Routing: Directs customer inquiries to optimal resources based on nature and complexity
- Banker Augmentation: Provides AI assistance to human bankers during customer interactions
- Knowledge Retrieval: Surfaces relevant information and procedures in context
- Decision Support: Guides complex financial discussions with data-backed insights
- Sales Journey Orchestration
- Intelligent Activation: Identifies optimal moments to introduce new products or services
- End-to-End Automation: Streamlines application and onboarding processes
- Personalized Journeys: Tailors sales processes to individual customer circumstances
- Contextual Cross-Selling: Embeds relevant offers within service interactions
- Relationship Expansion
- Share of Wallet Analysis: Identifies opportunity gaps in current customer relationships
- Life Event Detection: Recognizes major transitions (home purchase, education, retirement)
- Needs-Based Recommendations: Suggests products based on identified customer needs
- Loyalty Enhancement: Strengthens relationships through personalized engagement
Technical Implementation
- Agentic AI Architecture
- Employs specialized AI agents for different customer engagement functions
- Maintains consistent customer context across multiple agents
- Coordinates agent actions through centralized orchestration
- Operates within defined guardrails for regulatory compliance
- Omnichannel Delivery
- Enables consistent experience across digital and physical channels
- Supports seamless handoffs between self-service and human assistance
- Maintains conversation and context continuity across channels
- Personalizes channel selection based on customer preferences and journey stage
- Journey Analytics and Optimization
- Monitors full customer journeys across touchpoints
- Identifies friction points and abandonment patterns
- Tests journey variations to optimize outcomes
- Continuously refines engagement strategies based on feedback
Integration of These Core Components
The true innovation in Backbase’s platform appears to be the tight integration between these three core components:
Closed-Loop System
- Data → Analytics → Engagement → Data
- Creates a continuous improvement cycle where each customer interaction:
- Generates new data
- Refines predictive models
- Improves future engagement
- Produces more valuable data
- Creates a continuous improvement cycle where each customer interaction:
- Real-Time Learning
- Updates customer profiles and recommendations in real-time
- Adapts to changing customer circumstances immediately
- Maintains relevance in dynamic financial environments
- Cross-Functional Optimization
- Balances competing objectives (service efficiency, sales effectiveness, risk management)
- Optimizes for lifetime customer value rather than transactional outcomes
- Considers operational constraints in engagement decisions
Potential Implementation Challenges
Despite the sophisticated capabilities, banks implementing this platform may face several challenges:
- Data Quality and Completeness
- Banking data often suffers from inconsistency and fragmentation
- Historical data may lack the granularity needed for advanced analytics
- Customer consent management adds complexity to data utilization
- Model Governance
- Financial services require rigorous model validation and monitoring
- Explainability requirements may limit some advanced techniques
- Risk of algorithmic bias must be actively managed
- Change Management
- Requires significant shifts in banker roles and workflows
- Cultural adaptation to AI-augmented decision making
- Need for new skills and competencies across the organization
- Technical Debt
- Integration with legacy core banking systems can introduce complexity
- Potential performance constraints in real-time processing
- Scalability challenges during peak transaction periods
Strategic Implications
For banks considering this platform, several strategic considerations emerge:
- Differentiation Strategy
- How to preserve unique competitive advantages while using a platform solution
- Balancing standardization benefits with customization needs
- Developing proprietary AI extensions to the base platform
- Capability Development
- Building internal expertise to maximize platform benefits
- Balancing vendor dependence with in-house innovation
- Creating a roadmap for AI maturity advancement
- Value Measurement
- Establishing clear KPIs for platform impact
- Balancing short-term efficiency gains with long-term growth
- Attributing outcomes across complex customer journeys
Conclusion
Backbase’s AI-powered Banking Platform represents a sophisticated integration of data, analytics, and engagement capabilities that goes beyond traditional banking technology approaches. The platform’s potential to create a unified, intelligent banking experience offers significant opportunities for banks facing competitive pressures and customer expectations for personalized, frictionless service. However, successful implementation will require careful attention to data quality, change management, and strategic alignment to realize the full benefits of these advanced capabilities.
Personalization and Security in Backbase’s AI-Powered Banking Platform
Personalisation Revolution in Banking
Backbase’s AI-powered Banking Platform has the potential to fundamentally transform banking personalisation from generic segment-based approaches to truly individualised experiences. Here’s an in-depth analysis of how this personalisation might work:
1. Hyper-Individualised Customer Understanding
Multi-Dimensional Customer Profiles
- Financial DNA Mapping: Beyond traditional demographics and account data, the platform likely constructs comprehensive financial behavior patterns unique to each customer
- Contextual Awareness: Incorporates situational factors like location, time, device usage, and recent life events into customer profiles
- Preference Learning: Adaptively captures explicit and implicit preferences across channels, interactions, and decisions
- Temporal Evolution: Tracks how customer behaviors and needs evolve over time, creating a dynamic rather than static understanding
Behavioral Pattern Recognition
- Micro-Segmentation: Identifies nuanced customer archetypes based on hundreds of behavioral variables
- Financial Habit Detection: Recognizes recurring patterns in spending, saving, and financial management styles
- Decision-Making Style Analysis: Learns how individual customers approach financial decisions (analytical vs. emotional, risk-averse vs. opportunity-seeking)
- Channel and Timing Preferences: Identifies optimal engagement moments and methods for each customer
2. Adaptive Experience Orchestration
Journey Personalization
- Dynamic Journey Maps: Creates individualised customer journey paths rather than standard templates
- Real-Time Adaptation: Modifies journeys in progress based on customer signals and responses
- Milestone Recognition: Acknowledges and responds to significant customer achievements or challenges
- Contextual Next Steps: Suggests logical following actions based on individual circumstances
Interface Personalization
- Adaptive UX/UI: Customizes digital interfaces based on user behavior and preferences
- Information Prioritization: Surfaces the most relevant information for each customer
- Feature Accessibility: Promotes features based on individual usage patterns and needs
- Cognitive Load Management: Adjusts complexity and detail based on customer financial sophistication
3. Personalized Financial Guidance
Tailored Advisory Services
- Financial Goals Alignment: Suggests products and services directly tied to individual goals
- Personalized Insights: Generates observations about spending patterns, savings opportunities, or investment considerations specific to each customer
- Life Stage Guidance: Provides advice relevant to customer’s current and approaching life stages
- Custom Financial Education: Delivers financial literacy content calibrated to customer’s knowledge level and relevant topics
Proactive Opportunity Recognition
- Personalised Alerts: Notifies customers of relevant opportunities or risks based on their specific situation
- Timing Optimisation: Identifies ideal moments for financial decisions based on individual circumstances
- Need Anticipation: Predicts emerging financial needs before customers explicitly express them.
- Constraint Recognition: Acknowledges individual financial limitations in recommendations
Security in the Age of AI Banking
The increased personalisation and AI integration in banking bring both security challenges and opportunities. Here’s how Backbase’s platform likely addresses security concerns:
1. AI-Enhanced Fraud Protection
Behavioral Biometrics
- Interaction Pattern Analysis: Establishes baseline behavioral patterns in how customers navigate digital banking
- Continuous Authentication: Monitors subtle interaction patterns throughout sessions to detect anomalies
- Device Interaction Fingerprinting: Recognizes unique patterns in how individuals use their devices
- Adaptive Risk Scoring: Dynamically adjusts risk assessments based on behavioral deviations
Anomaly Detection
- Transaction Pattern Monitoring: Identifies deviations from established customer transaction patterns.
- Context-Aware Alerts: Considers location, device, time, and transaction type in risk assessment
- Network Analysis: Detects suspicious connections between accounts or transactions
- Multi-factor Pattern Recognition: Combines multiple weak signals to identify sophisticated fraud attempts
Predictive Fraud Prevention
- Attack Vector Anticipation: Predicts likely fraud approaches based on customer profile
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identifies potential security weaknesses in customer behaviour
- Preemptive Intervention: Implements additional security measures before high-risk activities
- Fraud Trend Adaptation: Rapidly updates detection models as new fraud patterns emerge
2. Secure AI Governance Framework
AI Security Architecture
- Model Integrity Protection: Safeguards against model poisoning or manipulation
- Secure Training Environments: Protects AI training processes from interference
- Input Validation: Rigorously validates all data inputs to AI systems
- Output Verification: Applies consistency and reasonableness checks to AI outputs
Explainable Security Decisions
- Transparent Risk Assessment: Provides clear explanations for security interventions
- Audit Trails: Maintains comprehensive records of AI security decisions
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures all automated security measures meet regulatory requirements
- Human Oversight: Enables appropriate human review of significant security actions
Data Privacy by Design
- Minimal Data Collection: Limits data gathering to necessary elements
- Privacy-Preserving Computation: Uses techniques like federated learning or differential privacy
- Data Anonymization: Removes personally identifiable information when possible
- Purpose Limitation: Restricts data usage to specific, predefined purposes
3. Secure Multi-Channel Integration
Channel Security Harmonization
- Consistent Security Standards: Applies uniform security policies across channels
- Cross-Channel Verification: Uses information from one channel to verify activity in another
- Secure Channel Transitions: Maintains security context during channel switches
- Risk-Based Authentication: Adjusts authentication requirements based on channel risk profile
Secure Open Banking Integration
- API Security Framework: Implements robust security for third-party integrations
- Partner Risk Assessment: Evaluates security posture of connected services
- Data Minimization: Limits data sharing to essential elements
- Consent Management: Provides granular customer control over data sharing
4. Human-AI Security Collaboration
Augmented Security Operations
- AI-Assisted Investigation: Supports security analysts with AI-generated insights
- Pattern Recognition Support: Helps identify complex security patterns
- Case Prioritisation: Directs human attention to the highest-risk situations
- Intelligent Alert Management: Reduces false positives through AI filtering
Security Experience Design
- Friction-Right Security: Balances security needs with customer experience
- Contextual Security Measures: Adjusts security interventions based on risk level
- Intuitive Security Interfaces: Makes security actions clear and straightforward
- Educational Security: Helps customers understand security measures and best practices
Integration of Personalization and Security
The most innovative aspect of Backbase’s approach may be how it integrates personalization and security rather than treating them as competing priorities:
1. Personalized Security Models
Individual Risk Profiles
- Customer-Specific Baselines: Establishes normal behavior patterns for each customer
- Personalized Risk Thresholds: Adjusts security sensitivity based on individual risk profiles
- Adaptive Authentication: Tailors authentication methods to customer preferences and risk level
- Security Journey Mapping: Creates personalized security paths based on customer characteristics
Context-Aware Protection
- Situational Risk Assessment: Evaluates security needs based on transaction context
- Relationship-Based Trust: Incorporates established behavior patterns into risk calculations
- Value-Based Security: Scales security measures to transaction significance
- Progressive Security: Gradually introduces additional security based on activity risk
2. Security-Enhanced Personalisation
Trust-Based Experiences
- Security-Awareness in Recommendations: Incorporates security considerations into personalised offers.
- Trust-Building Features: Highlights security elements that matter most to individual customers
- Safety-First Design: Ensures personalisation doesn’t compromise security fundamentals
- Transparent Data Usage: Clearly communicates how customer data informs personalisation
Security as Personalization
- Security Feature Customization: Allows customers to tailor security preferences
- Individual Security Dashboards: Provides personalized visibility into security status
- Security Communication Preferences: Adapts security alerts and notifications to customer preferences
- Personalized Security Education: Delivers relevant security guidance based on customer behavior
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
Despite the impressive potential, several challenges must be addressed when implementing these capabilities:
Regulatory Compliance
- Data Protection Regulations: Must navigate PDPA in Singapore and regional variations
- Algorithmic Accountability: Need for demonstrable fairness and absence of bias
- Explainability Requirements: Ability to justify automated decisions to regulators
- Cross-Border Data Governance: Managing compliance across international operations
Ethical Considerations
- Privacy Boundaries: Determining appropriate limits for personalization
- Manipulation Concerns: Ensuring personalization doesn’t exploit vulnerabilities
- Inclusion and Accessibility: Avoiding digital discrimination or exclusion
- Transparency Requirements: Clearly communicating how AI influences banking experiences
Technical Integration
- Legacy System Compatibility: Integrating advanced capabilities with existing infrastructure
- Data Quality Dependencies: Ensuring sufficient data quality for reliable personalisation
- Real-Time Performance: Maintaining speed and responsiveness with complex processing
- Incremental Implementation: Balancing quick wins with long-term transformation
Conclusion: The Future of Personal and Secure Banking
Backbase’s AI-powered Banking Platform represents a vision of banking where personalisation and security are mutually reinforcing rather than competing priorities. This integration could fundamentally transform banking relationships by creating experiences that feel simultaneously more human and more secure.
For Singapore banks specifically, this approach aligns well with national priorities around digital transformation, customer centricity, and cybersecurity excellence. The platform’s capabilities could help Singapore maintain its position as a financial innovation hub while addressing growing customer expectations for both personalised service and robust security.
However, successful implementation will require careful attention to regulatory compliance, ethical considerations, and technical integration challenges. Banks that thoughtfully navigate these complexities while leveraging the platform’s capabilities can establish new standards for what constitutes an excellent banking experience in the AI era.
pplication of Gen AI, Fintech, and Banking Dynamics to Singapore
Singapore presents a fascinating case study for the relationship between generative AI, fintech, and traditional banking due to its unique positioning as both a global financial hub and a technology innovation centre.
Singapore’s Current Landscape
- Strong Financial Infrastructure: Singapore hosts numerous global banks and financial institutions with established operations.
- Robust Regulatory Framework: The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has developed a reputation for forward-thinking but prudent regulation.
- Government-Backed Innovation: Initiatives like Singapore’s AI Strategy and the Financial Sector Technology & Innovation (FSTI) scheme actively promote fintech development.
- Talent Hub: Singapore attracts global AI and financial talent through education initiatives and immigration policies.
Key Singapore-Specific Dynamics
- MAS as Innovation Catalyst: Unlike some regulators who primarily restrict, MAS often acts as an enabler by:
- Creating regulatory sandboxes for fintech experimentation
- Publishing AI governance frameworks specific to financial services
- Launching initiatives like Project Ubin for blockchain exploration
- Bank-Fintech Integration Already Advanced: Singapore’s banks have pursued aggressive digitalization:
- DBS Bank’s digital transformation and API platform
- OCBC’s AI lab and fintech partnerships
- UOB’s engagement with AI startups
- Government Data Initiatives: Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative and National AI Strategy provide infrastructure for data sharing that benefits AI development.
Singapore Opportunities
- Regional AI Hub: Singapore is positioned to become ASEAN’s center for financial AI development, with models that can be exported to neighboring markets.
- Regulatory Innovation: MAS could pioneer balanced Gen AI regulation that other jurisdictions may follow.
- Cross-Border Finance: Singapore’s position as a cross-border financial center creates unique opportunities for AI in areas like:
- Multi-currency transactions and management
- Cross-border compliance automation
- International identity verification
- Green Finance: Combining Singapore’s sustainability focus with AI to develop tools for ESG investing and carbon footprint tracking.
Singapore-Specific Challenges
- Data Privacy Balance: Navigating Singapore’s Personal Data Protection Act while enabling AI innovation.
- Regional Market Adaptation: Ensuring AI models developed in Singapore can adapt to diverse ASEAN markets.
- Talent Competition: Competing globally for limited AI expertise despite Singapore’s small population.
- Trust in AI Systems: Maintaining Singapore’s reputation for stability and trustworthiness while implementing new technologies.
Strategic Recommendations for Singapore
- Specialized AI Governance Framework: Develop financial sector-specific AI guidelines that balance innovation with Singapore’s reputation for stability.
- Regional Data Partnerships: Establish cross-border data-sharing agreements with ASEAN neighbors to enrich AI training datasets.
- AI Education Integration: Further integrate AI skills development into Singapore’s educational institutions and professional certification processes.
- Fintech-Bank Collaboration Platforms: Create structured programs to facilitate partnerships between traditional banks and AI-focused startups.
Singapore’s combination of strong governance, technological infrastructure, and financial expertise positions it uniquely to become a global leader in the integration of generative AI into financial services—potentially creating models that could be adopted internationally.
AI is delivering tangible benefits, including:

Processing massive datasets at speeds exceeding human capabilities
Reducing operational costs
Improving regulatory compliance
Enhancing strategic decision-making
Transforming treasury management through improved cash flow prediction
Generative AI represents the next wave of innovation:
Over 40% of organizations are piloting or using generative AI in finance
Applications include producing comprehensive narratives, analyzing complex datasets, and scenario-based forecasting
Nearly all surveyed organizations plan to implement generative AI within three years
Return on investment is significant:
57% of “AI leaders” report AI investments exceeding expectations
Leading organizations embed AI across multiple functions rather than using it in silos
Challenges remain in several areas:
Data security and privacy concerns
Integration complexities with legacy systems
Ethical considerations and potential algorithmic bias
Talent shortages in AI specialisations
Future outlook:
AI will enable more personalized customer experiences
Enhanced fraud detection capabilities
Creation of new business models and revenue streams

AI Transformations & Algorithm Functions in Banking
Based on the article, here’s an analysis of the key AI transformations and algorithm functions revolutionising the banking sector:
Data Processing & Analysis

- Pattern Recognition: AI algorithms process massive datasets to identify patterns that humans might miss
- Anomaly Detection: Systems flag unusual transactions that deviate from established patterns
- Real-time Insights: Continuous monitoring and analysis of financial data streams
Treasury Management

- Cash Flow Prediction: AI has replaced complex spreadsheets with tools that forecast cash flows in seconds
- Economic Scenario Simulation: Algorithms model various economic conditions to inform decision-making
- Liquidity Optimization: Systems help optimize liquidity management through predictive modeling
Generative AI Applications

- Narrative Creation: Automatically generating comprehensive financial reports and analyses
- Scenario Forecasting: Modeling potential outcomes across multiple variables
- Geopolitical Impact Analysis: Assessing financial implications of global political developments
- Document Analysis: Streamlining the review and extraction of information from financial documents
Risk & Compliance
- Fraud Detection: Identifying potentially fraudulent activities through pattern analysis
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to complex regulatory frameworks
- Performance Evaluation: Assessing financial performance against benchmarks and predictions

Cross-Functional Implementations
- Accounting Automation: Streamlining accounting processes through AI-powered systems
- Tax Preparation: Simplifying and optimizing tax compliance procedures
- Procurement Optimization: Enhancing vendor selection and purchasing processes
Strategic Decision Support
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting trends and outcomes to inform strategic planning
- Investment Decision Support: Providing data-driven insights for investment allocation
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and quantifying potential risks across operations

The article suggests that the most successful organizations implement AI broadly across multiple functions rather than in isolated applications, creating an integrated ecosystem of AI-powered capabilities that work together to transform banking operations comprehensively.
AI Transformations in Singapore’s Banking Sector
Based on the article’s insights, here’s how AI transformations and algorithmic functions could specifically apply to Singapore’s banking landscape:

Strategic Relevance for Singapore
Singapore is uniquely positioned to benefit from AI in banking due to:
- Its status as a global financial hub
- Strong regulatory framework under MAS (Monetary Authority of Singapore)
- Advanced digital infrastructure
- High technology adoption rates
- Position as an APAC financial technology leader

Key Applications for Singapore Banks
Enhanced Financial Intelligence
- AML/KYC Compliance: AI algorithms could strengthen Singapore’s already robust anti-money laundering frameworks
- Cross-border Transaction Monitoring: Critical for Singapore as an international banking hub
- Real-time Fraud Detection: Particularly valuable for Singapore’s high-volume payment systems

Treasury and Liquidity Management
- Regional Treasury Operations: AI optimization for banks managing liquidity across ASEAN markets
- SGD Currency Flow Prediction: Specialized models for Singapore’s currency movements
- MAS Regulatory Compliance: Automated adherence to Singapore-specific banking regulations
Personalised Banking Services
- Multi-Language Customer Service: AI-powered solutions catering to Singapore’s multilingual population
- Customised Wealth Management: Algorithmic solutions for Singapore’s growing wealth management sector
- SME Banking Solutions: Tailored AI applications for Singapore’s vital SME sector
Regional Financial Analysis
- ASEAN Market Intelligence: Generative AI producing insights on regional market movements
- Geopolitical Risk Assessment: Analysing the impacts of regional tensions on Singapore’s financial position
- Trade Finance Optimisation: Algorithmic improvements to Singapore’s significant trade finance operations

Implementation Considerations for Singapore
Data Protection Compliance
- AI systems would need to comply with Singapore’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA)
- Adherence to MAS Technology Risk Management Guidelines

Talent Development
- Leverage Singapore’s educational institutions for AI talent development
- Potential partnerships with government initiatives like AI Singapore
Cross-Border Collaboration
- AI systems that facilitate Singapore’s role as a connector between Western and Asian financial markets
- Standardised protocols for data sharing with international banking partners

Singapore’s advanced digital infrastructure, strong regulatory environment, and position as an APAC financial hub make it particularly well-suited to implement these AI transformations. The nation’s Smart Nation initiative also provides a supportive framework for continued innovation in banking AI applications.
Comprehensive Approach
The guide correctly emphasizes that no single method provides complete protection. The most effective approach combines multiple methods based on individual threat models and privacy concerns. The recommended combination of tools addresses different aspects of privacy:
- Data in transit (VPNs, secure email)
- Data at rest (antivirus, updates, backups)
- Authentication (password managers)
- Behavioural practices (mindful sharing)
- Existing data exposure (data removal tools)
This layered approach is consistent with cybersecurity best practices and provides defense in depth against various privacy threats.
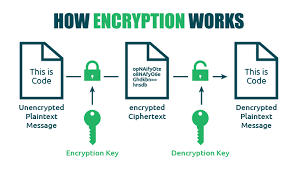
How Encryption Works

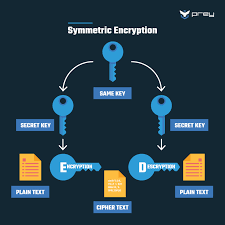
Encryption uses mathematical algorithms to convert plaintext (readable data) into ciphertext (scrambled data). Only those with the decryption key can convert the ciphertext back into usable information. There are two main types:
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. It’s efficient but requires a secure key exchange.
- Asymmetric Encryption uses a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption—to allow secure communication without prior key exchange.
Key Encryption Applications for Privacy
Device Encryption
- Full-disk encryption: Protects all data on your computer or smartphone (BitLocker for Windows, FileVault for Mac, and built-in encryption for iOS and Android)
- File-level encryption: Protects individual files and folders

Communication Encryption
- HTTPS: Secures website connections (look for the padlock icon in your browser)
- End-to-end encryption: Used in messaging apps like Signal, WhatsApp, and others to ensure only you and your recipient can read messages
- Email encryption: Options include PGP (Pretty Good Privacy), S/MIME, or encrypted email services
Network Encryption
- VPNs: Create an encrypted tunnel for all your internet traffic
- Wi-Fi encryption: WPA3 is the current most substantial standard for wireless networks
Cloud Storage Encryption
- At-rest encryption: Protects stored data
- Zero-knowledge encryption: The provider has no access to your encryption keys
- Client-side encryption: Data is encrypted before leaving your device

Implementing Encryption in Your Digital Life
- Enable device encryption on all your computers and mobile devices
- Use encrypted messaging apps for sensitive communications
- Verify HTTPS connections when sharing personal or financial information
- Consider encrypted email for sensitive communications
- Choose cloud services with strong encryption policies
- Use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks
- Password-protect and encrypt sensitive files and backups
Limitations to Consider
- Encryption can’t protect against malware already on your device
- Weak passwords can undermine even the strongest encryption
- Encryption doesn’t hide metadata (who you’re communicating with, when, how often)
- Some countries have laws limiting encryption use or requiring backdoors

Encryption is a fundamental aspect of digital privacy that works best as part of a comprehensive security strategy. By understanding and implementing appropriate encryption methods, you can significantly enhance your online privacy protection.
.
Identity Theft
Identity theft is a pervasive form of fraud that can have devastating consequences for victims. In this crime, the perpetrator steals an individual’s personal information to assume their identity. This stolen information can often be gathered from discarded documents such as bank statements, utility bills, or even phishing scams.
Once armed with this data, the criminal may choose to open accounts in the victim’s name, a process known as application fraud. They might apply for credit cards, loans, or utility services under pretences, leaving the unsuspecting victim to deal with the aftermath.
The emotional toll of identity theft can be immense. Victims often face financial losses and damage to their credit scores, which can take years. In today’s digital age, account takeovers have become a prevalent threat to unsuspecting victims. Criminals typically employ tactics such as phishing, vishing, or smishing to manipulate individuals into revealing their personal information.

Phishing often involves deceptive emails that appear to come from legitimate sources. These emails may prompt the victim to click on malicious links or provide sensitive details under the guise of verifying their identity.
Vishing, or voice phishing, involves phone calls in which scammers impersonate bank representatives or trusted entities to extract confidential information directly from the victim. Similarly, smishing involves text messages that lure individuals into divulging critical data.
Once armed with this personal information, the criminal can easily convince a bank to change the account holder’s address. This deception allows them full access to the victim’s financial accounts and resources.

Additionally, some criminals are skilled enough to bypass bank interaction altogether. They can use the obtained credentials to log into online accounts directly, executing unauthorised transactions without needing any further verification.
The consequences for victims can be devastating, leading not only to financial loss but also to emotional distress as they recover their stolen identities and secure their accounts. Consequently, individuals must remain vigilant and understand these risks to protect themselves against potential account takeovers for repair. Additionally, they may find themselves tangled in legal disputes as they try to prove their innocence.

Recovering from such a violation requires diligence and time, making it crucial for individuals to safeguard their personal information vigilantly. Implementing measures like shredding sensitive documents and monitoring credit reports can help prevent these types of crimes before they occur.
Maxthon
Maxthon has set out on an ambitious journey aimed at significantly bolstering the security of web applications, fueled by a resolute commitment to safeguarding users and their confidential data. At the heart of this initiative lies a collection of sophisticated encryption protocols, which act as a robust barrier for the information exchanged between individuals and various online services. Every interaction—be it the sharing of passwords or personal information—is protected within these encrypted channels, effectively preventing unauthorised access attempts from intruders.
 This meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
This meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
In today’s rapidly changing digital environment, Maxthon’s unwavering commitment to ongoing security enhancement signifies not only its responsibility toward users but also its firm dedication to nurturing trust in online engagements. With each new update rolled out, users can navigate the web with peace of mind, assured that their information is continuously safeguarded against ever-emerging threats lurking in cyberspace.
