A man lost his life after he stopped responding on a roller coaster at Orlando’s Epic Universe theme park.
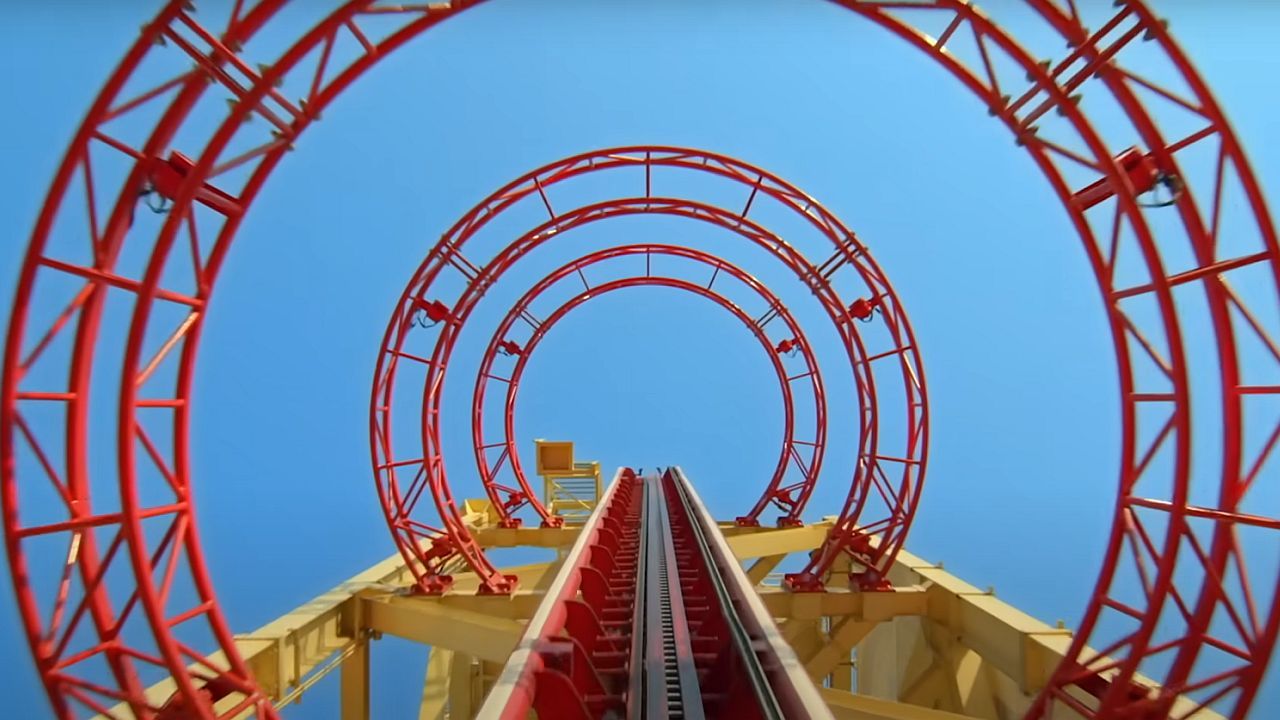
The incident happened on Stardust Racers. This ride sits in Celestial Park. Celestial Park forms one of five main areas in the fresh Universal Epic Universe in Orlando.
Reports show that 32-year-old Kevin Rodriguez Zavala passed away on September 17, 2025. He rode the coaster that evening. Soon after, he became unresponsive. Medics rushed him to a nearby hospital. There, doctors declared him dead. Officials have not shared the cause of death yet.
Kevin Rodriguez Zavala stood at 32 years old. He finished the ride but then went still. Rescue teams acted fast. They pulled him from the train. Paramedics tried to help on site. Still, he did not recover. His trip to the hospital ended in tragedy.
Stardust Racers marks Universal’s longest coaster to date. It uses two racing trains that zip along side by side. Each train hits 62 miles per hour. That’s the same as 100 kilometers per hour. The ride climbs to 40.5 meters high. Its track stretches 1.5 kilometers. Riders get a rush from the dueling setup. The twin paths twist and cross each other. This design makes the race feel real and intense. No other coaster from Universal matches its length or speed combo.
The park placed this ride in Celestial Park. That area draws from starry skies and cosmic wonders. Epic Universe opened four months back. It cost $7 billion to build. This spot stands as the first big new theme park in Central Florida in 26 years. Five themed zones fill the space. They include Celestial Park plus areas like Super Nintendo World and the Wizarding World of Harry Potter. A 500-room hotel sits right there too. Guests flock to it for full-day fun.
Now, the Orange County Sheriff’s Office started a probe. They aim to find out what went wrong. Universal staff pledged full help to the team. The park stayed open the next day, September 18. But they shut down Stardust Racers for checks. Safety comes first in these cases.
Universal leaders shared their shock. They called the event heartbreaking. The company sent deep regrets to Kevin’s family and friends. Such losses hit hard in a place built for joy.
This story unfolds as experts dig deeper. The probe looks at ride safety and rider health. Theme parks follow strict rules to keep visitors safe. Rides like Stardust Racers pass daily tests. Yet rare events like this spark questions. Readers might wonder about ride checks or health rules before boarding. Universal requires riders to meet height and health standards. Still, details on Kevin’s case remain private for now. As more facts come out, the public will learn the full picture.

The Hidden Dangers: Understanding Amusement Park Ride Hazards
The recent tragic death at Universal’s Epic Universe serves as a stark reminder that beneath the thrills and excitement of modern amusement parks lie genuine risks that can have devastating consequences. While millions of riders enjoy theme park attractions safely each year, understanding the various hazards associated with these mechanical marvels is crucial for both operators and the riding public.
The Scale of the Industry and Risk
The global amusement park industry serves over 400 million visitors annually, with the vast majority experiencing rides without incident. According to the International Association of Amusement Parks and Attractions (IAAPA), the chance of serious injury on a ride is approximately 1 in 15.5 million rides taken. However, when incidents do occur, they can range from minor injuries to fatalities, making risk assessment and mitigation paramount.
Primary Categories of Ride Hazards
Mechanical Failures
Mechanical failures represent one of the most serious categories of ride hazards, as they can occur suddenly and without warning to riders.
Structural Failures: These involve the breakdown of essential ride components such as support beams, track sections, or foundations. Modern roller coasters experience enormous forces—riders can experience up to 6 G-forces on some attractions—placing tremendous stress on structural elements. Metal fatigue, inadequate maintenance, or design flaws can lead to catastrophic failures.
Restraint System Malfunctions: Safety restraints are the primary barrier between riders and serious injury or death. Hydraulic failures in shoulder harnesses, mechanical problems with lap bars, or electronic malfunctions in computerized restraint systems can leave riders inadequately secured during high-force maneuvers.
Control System Failures: Modern rides rely heavily on computerized control systems to manage speed, braking, and block zones (sections of track that prevent collisions). Software glitches, sensor failures, or communication breakdowns between control systems can lead to dangerous situations, including trains colliding or failing to stop appropriately.
Human Factors and Operational Hazards
Operator Error: Ride operators are the final human checkpoint in the safety chain. Inadequate training, fatigue, distraction, or failure to follow protocols can result in serious incidents. This includes improper restraint checks, failing to observe rider safety requirements, or incorrect ride operation procedures.
Guest Behavior Risks: Many incidents involve guests who fail to follow safety instructions. This includes standing up during rides, extending limbs outside safety barriers, bringing prohibited items, or attempting to exit rides during operation. Intoxication, medical conditions that guests fail to disclose, or deliberate risk-taking behavior compound these hazards.
Maintenance and Inspection Failures: Rides require rigorous daily, weekly, and annual maintenance schedules. Deferred maintenance, inadequate inspection protocols, or failure to identify wear patterns can allow dangerous conditions to develop gradually until they result in sudden failures.
Design and Engineering Hazards
G-Force Related Injuries: Roller coasters and spinning rides subject riders to significant gravitational forces. Excessive positive G-forces can cause blackouts, while negative G-forces can lead to injuries from riders being lifted from their seats. Lateral forces in turns can cause neck injuries or bruising from restraints.
Sudden Acceleration and Deceleration: Launch coasters that accelerate from 0 to 100+ mph in seconds, or rides with sudden stops, can cause whiplash, back injuries, or exacerbate existing medical conditions. The human body has limits for how quickly it can safely change velocity.
Height and Fall Hazards: Beyond the obvious risks of falls from elevation, height-related hazards include objects falling from rides onto guests below, wind effects at elevation, and psychological effects that can cause panic or medical emergencies in susceptible individuals.
Environmental and External Hazards
Weather-Related Risks: Lightning poses an extreme danger to tall rides and their occupants. High winds can affect ride operation and safety, while rain can create slippery surfaces and affect braking systems. Temperature extremes can affect both mechanical components and rider safety.
External Factors: Power outages can strand riders at height or disable safety systems. Seismic activity, though rare, can affect ride structures. Even wildlife interactions, such as birds striking riders on high-speed coasters, represent documented hazards.
Specific Ride Type Hazards
Roller Coasters
Modern roller coasters present unique hazard profiles based on their design:
High-Speed Coasters: Rides reaching speeds over 70 mph face risks from wind resistance, aerodynamic effects, and the increased severity of any malfunction. The kinetic energy involved in high-speed operations means that any failure has potentially catastrophic consequences.
Inverted and Suspended Coasters: These rides hang passengers below the track, creating unique restraint challenges and increased consequences for any restraint failure. The inverted position can also cause medical issues for some riders.
Launch Coasters: Hydraulic, pneumatic, or magnetic launch systems can fail catastrophically. The rapid acceleration can cause medical emergencies in riders with pre-existing conditions, and mechanical failures during launch can result in trains not completing the circuit.
Spinning Rides
Centrifugal Force Risks: Rides like tilt-a-whirls or spinning coasters create complex force vectors that can cause disorientation, motion sickness, and in extreme cases, loss of consciousness. The combination of spinning motion with other movements multiplies these effects.
Mechanical Complexity: Spinning rides often have complex gear systems and multiple moving parts, increasing the potential points of failure compared to simpler ride designs.
Water Rides
Drowning Hazards: Water rides present unique risks, particularly for non-swimmers or during equipment failures that trap riders in water. Even shallow water can pose drowning risks if riders become unconscious or trapped.
Rapids and Flow Dynamics: Artificial rapids can create unpredictable water conditions that may overwhelm safety systems or create hydraulic effects that trap objects or people.
Medical and Health Hazards
Pre-existing Conditions
Many ride injuries involve guests with pre-existing medical conditions that are exacerbated by the ride experience:
Cardiovascular Issues: The excitement and physical stress of rides can trigger heart attacks, strokes, or other cardiovascular events in susceptible individuals. High G-forces place additional strain on the cardiovascular system.
Pregnancy Risks: Pregnant women face unique risks from the forces and motions of rides, which can potentially cause complications or injury to both mother and fetus.
Musculoskeletal Vulnerabilities: Individuals with back problems, neck injuries, or other musculoskeletal issues may experience severe aggravation of their conditions during rides, particularly those with sudden directional changes or high forces.
Ride-Induced Medical Emergencies
Motion Sickness and Disorientation: Beyond simple nausea, severe motion sickness can lead to dehydration, falls, or panic reactions that create additional safety hazards.
Psychological Reactions: Panic attacks, claustrophobia, or other psychological responses can cause riders to attempt dangerous actions like trying to exit a moving ride or removing safety restraints.
Regulatory Framework and Safety Standards
Industry Standards
The amusement ride industry operates under a complex web of safety standards developed by organizations like ASTM International, which publishes comprehensive guidelines for ride design, manufacturing, operation, and maintenance. These standards cover everything from structural engineering requirements to operator training protocols.
Inspection and Certification
Most jurisdictions require regular third-party inspections of rides, with daily operational checks, periodic detailed inspections, and annual comprehensive evaluations. However, the quality and frequency of these inspections can vary significantly between different regulatory authorities.
Incident Reporting and Analysis
When incidents occur, thorough investigation and reporting help identify trends and prevent future occurrences. However, not all jurisdictions have robust incident reporting requirements, and some incidents may go unreported or uninvestigated.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Engineering Solutions
Redundant Safety Systems: Modern rides incorporate multiple backup systems for critical components. Block zones prevent train collisions, multiple independent braking systems ensure stops are possible even with component failures, and computer systems have backup processors and fail-safe modes.
Advanced Materials and Testing: The use of high-strength materials, computer-aided stress analysis, and non-destructive testing methods helps identify potential failures before they occur. Regular materials testing can detect metal fatigue or stress concentration before catastrophic failure.
Design for Human Factors: Ride restraints and control systems are increasingly designed to account for human behavior and limitations. This includes restraints that accommodate a wide range of body sizes and types, and control systems that prevent operator errors.
Operational Improvements
Enhanced Training Programs: Comprehensive operator training that includes not just procedural knowledge but also understanding of safety systems, emergency procedures, and the ability to recognize and respond to unusual situations.
Maintenance Excellence: Proactive maintenance programs that exceed minimum requirements, with detailed record-keeping and trend analysis to identify components that may need replacement before failure occurs.
Guest Education and Screening: Clear communication of ride requirements and restrictions, along with effective screening procedures to identify guests who should not ride due to medical conditions or other risk factors.
The Future of Ride Safety
Technological Advances
Predictive Maintenance: Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and artificial intelligence are beginning to enable predictive maintenance systems that can identify potential failures before they occur, allowing for proactive replacement or repair of components.
Enhanced Monitoring Systems: Real-time monitoring of ride forces, guest vital signs, and system performance can help identify problems immediately and potentially prevent incidents from becoming tragedies.
Virtual Reality and Simulation: Advanced simulation systems allow for extensive testing of ride systems and emergency scenarios without putting real guests at risk, improving both design and training.
Regulatory Evolution
Safety regulations continue to evolve in response to new technologies, incident investigations, and improved understanding of risk factors. The challenge lies in balancing innovation in ride design with prudent safety requirements.
Conclusion
The amusement park industry’s safety record is remarkably good considering the number of people who enjoy rides annually and the complex mechanical systems involved. However, the inherent hazards of these attractions—from mechanical failures and human factors to medical emergencies and environmental risks—require constant vigilance from designers, operators, regulators, and riders themselves.
Recent incidents like the tragedy at Epic Universe remind us that behind every thrilling ride experience lies a complex web of engineering, maintenance, operation, and safety systems that must work flawlessly to protect guests. While we cannot eliminate all risks, understanding these hazards is the first step in continuing to improve safety standards and prevent future tragedies.
The goal should not be to eliminate all risk—which would eliminate the thrill that makes these attractions appealing—but rather to manage and minimize risks through superior engineering, rigorous maintenance, comprehensive training, and intelligent regulation. Only through this multi-faceted approach can the industry continue to provide safe thrills for millions of guests while learning from each incident to prevent future occurrences.
As technology advances and our understanding of risk factors improves, the amusement park industry must remain committed to putting safety first, even when faced with competitive pressures to create more extreme and thrilling experiences. The true measure of success in this industry should not just be the screams of delight from satisfied customers, but the safe return of every guest to their families at the end of the day.
What is intrusive target advertising?
Understanding and addressing data privacy concerns is essential. Marketers collect customer data, such as demographical and behavioural information, as you engage with their brand. This information is collected via cookies, location information and search data. With this information, marketers can identify their target segment and create personalised marketing messages and visuals to interact and engage.
Intrusive target ads occur when your digital footprint is collected without your permission or unknowingly. Google, one of the world’s most used search engine giant, has been in multiple lawsuits related to unethical methods of data collection of their user’s information.
As a consumer, intrusive advertisement can negatively impact your online experience when advertisements are bombarded at you on different platforms.
How to avoid intrusive advertising?
Unethical data collection has been a hot topic as information collected can expose individuals to dangerous scenarios. As a result, different parties have gotten involved to ensure data collected complies with laws and regulation or allow users to have the option to opt out of having their data collected.
1. Government
Data privacy involves protecting and responsibly using an individual’s personal information, preferences, and activities. With the increase in online customer data, measures have been implemented to safeguard personally identifiable information (PII) like names, dates of birth, email addresses, financial details, and browsing history.
Governments and organisations worldwide are implementing measures to protect personal information, and marketers must comply with data collection regulations. Stay informed about these regulations to ensure compliance.
GDPR privacy laws
GDPR, a data privacy law, has changed how marketers work. It gives people more control over their data and requires businesses to ask for explicit permission before using it. Marketers must now be transparent about data collection and update their privacy policies to comply.
One challenge is explaining how data is used and giving people the choice to opt in or out. This complicates targeting and personalisation efforts, as marketers need permission to use data. GDPR also requires companies to respond to requests from customers to access or delete their data promptly and correctly. Marketers must be prepared to handle these requests to follow the law.
Privacy laws are changing in the US as data privacy becomes more important worldwide. While the US doesn’t have a national privacy law like the EU’s GDPR, individual states are taking steps to protect people’s privacy. California has the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) since January 2020.
This law lets Californians know what data companies collect about them and who they share it with and allows them to delete it. People can also choose not to have their information sold to others. Other states, like Virginia, are following California’s example. Virginia passed the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) in March 2021, giving its residents more control over their data, including the right to transparency, access, deletion, and opting out.
2. Private businesses
Apple’s privacy updates are causing challenges for marketers. One example is the Mail Privacy Protection (MPP) feature, which opens incoming emails to protect user privacy. This feature hides IP addresses and prevents tracking of the recipient’s location and online activity. Apple’s recent iOS 17 updates also focus on protecting user data and privacy, making it harder for marketers to track engagement.
For instance, Link Tracking Protection in iOS 17 removes tracking parameters from messages, mail, and links, making it difficult to link interactions to specific users. Despite these challenges, link tracking remains a helpful metric, with only certain link types being affected.
Ensuring ethical data collection practices is essential for fostering trust with customers. When customers are hesitant to share their data, it can hinder their overall experience.
3. Yourself
You can also play a part to protect your own online data privacy through methods such as using private browsers such as Maxthon that prioritises data privacy of their users. Maxthon browser prioritizes data privacy by incorporating advanced encryption measures to protect users’ personal information. It ensures that user data is anonymized and not shared with third parties without consent.
By minimizing data collection, Maxthon reduces the risk of potential security breaches or privacy violations. Additionally, the browser offers robust privacy settings that allow users to control what information is collected and stored.
Maxthon takes a proactive approach to enhancing security and protecting user privacy by minimizing the collection of unnecessary data. By reducing the amount of personal information gathered, the risk of potential security breaches or privacy violations is significantly lowered. Additionally, Maxthon provides users with robust privacy settings that allow for greater control over their online activities.
These privacy settings include options to block unwanted tracking cookies, enable private browsing mode, and customize cookie permissions on a site-by-site basis. Users can also choose to opt-out of personalized advertisements and prevent websites from accessing their location or webcam without permission. With these features in place, Maxthon ensures that users can browse the internet securely and with peace of mind knowing their data is protected.
Maxthon, as a leading web browser, understands the importance of protecting user data. To ensure the highest level of security, the company conducts regular audits to assess its data protection measures. These audits help identify any potential vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry standards. Additionally, Maxthon focuses on implementing timely security updates to address any emerging threats or issues.
By staying proactive in evaluating its data protection practices, Maxthon demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding user information. The company prioritizes staying informed about the latest security trends and technologies to enhance its defenses against cyber threats. Through these continuous efforts, Maxthon aims to provide users with a secure browsing experience that instills trust and confidence in their data privacy.
Through regular audits and security updates, Maxthon constantly evaluates its data protection practices to adhere to the latest industry standards. Users can also benefit from features like built-in ad blockers and anti-tracking tools for a more secure browsing experience. Overall, Maxthon puts an emphasis on maintaining user trust through transparent data handling policies and proactive measures to safeguard sensitive information.
