In our increasingly digital world, a surprising number of individuals remain blissfully unaware of the myriad ways their personal information is collected, utilised, and disseminated. This lack of awareness can leave them vulnerable as they navigate a landscape where their data holds significant value. However, there are proactive measures one can take to safeguard personal information and maintain privacy in this interconnected realm.
Picture this: every click you make, every search you conduct, and every interaction online generates a wealth of information about you. This encompasses not just your basic details but also insights into your habits, preferences, and lifestyle choices. As you traverse the internet, it’s crucial to arm yourself with knowledge about how to shield your sensitive information from prying eyes.
Let’s delve into the world of data sharing. Data is a prized asset; thus, exercising caution when engaging with companies and applications is essential. You must be discerning in your choices, ensuring you understand who will have access to your data and under what circumstances.
Consider the various categories of information that may be collected about you:
- Personal Information: This includes sensitive identifiers such as your Social Security number or driver’s license number—data that could lead to identity theft if mishandled.
- Behavioural Data: This encompasses a broader spectrum—your health records, daily activities, interests, and even behavioural patterns that companies can analyse to tailor services or advertisements.

In today’s digital landscape, many platforms request extensive access to your personal information before allowing you to utilise their services. Some may ask for your location, contacts, or even photos long before you’ve had a chance to explore what they truly offer. While certain services might genuinely require this access for functionality, others may seek unnecessary data that does not enhance your experience.
Before handing over any personal details, take a moment to assess the nature of the request. Ask yourself: Is this information genuinely essential for the service I wish to engage with? Will sharing it yield any tangible benefits? Be cautious; some applications may seek permissions unrelated to the services they provide.
When contemplating the installation of a new app or the use of an unfamiliar service, it’s prudent to investigate the privacy and security settings available. Most devices allow you to customise these settings, enabling you to share only the minimum amount of information required for the service at hand. Remember that each device, application, or web browser has its own set of privacy controls, so it’s wise to review these settings regularly.
Furthermore, take stock of your social media profiles and applications; ensure they reflect your desire for privacy. If there are applications cluttering your device that you no longer use, don’t hesita to e—delete them! Keeping only those tools that serve a purpose in your life not only streamlines your digital experience but also reduces potential vulnerabilities.
In this vast digital ecosystem, knowledge is power. By taking deliberate steps to protect your personal information, you can navigate the online world with greater confidence and security.
The Importance of Strong Passwords and the Role of Password Managers

In a digital world where our identities, finances, and personal information are increasingly at risk, compromised passwords have emerged as one of the primary avenues through which cybercriminals can infiltrate our lives. Research conducted by NordPass reveals a staggering statistic: the average individual is burdened with the task of remembering around 100 different passwords. This overwhelming number often leads people to adopt the risky habit of reusing passwords across multiple accounts—a practice that many are well aware poses significant dangers yet continue to engage in nonetheless.
Fortunately, there is a straightforward remedy to this predicament: the use of a reliable password manager. Imagine having the ability to create long, unique passwords for each of your accounts without the anxiety of having to memorise them all. A password manager acts as a secure vault, safeguarding your online credentials within an encrypted database that is protected by a single master password. This means that once you’ve input your login details into the password manager, the only password you need to retain in your memory is that all-important master password.
Picture this: no more struggling to recall countless combinations of letters, numbers, and symbols. Instead, you only have to remember one single phrase. Plus, many password managers come equipped with a nifty feature that auto-generates strong and distinctive passwords for you. So, whenever you decide to create a new account, the password manager will offer you the option to utilise a robust, randomly generated password—one that is virtually impossible for anyone to guess.
But the benefits don’t stop there; think about how much time you could save. Beyond merely protecting your passwords, these handy tools can automatically fill in your login credentials, allowing you to breeze through sign-ins with remarkable speed. Additionally, they can help expedite online shopping by auto-filling your personal information such as name, address, email, phone number, and even credit card details, making checkout processes smoother than ever.
One of the most valuable features of a password manager is its ability to safeguard against phishing attempts. If you happen to receive a deceptive email masquerading as a legitimate source—an attempt by fraudsters to trick you into revealing your credentials—your password manager will come to the rescue. It won’t auto-fill your information because it recognises that the site isn’t associated with any of your saved passwords.
Moreover, today’s password managers often boast compatibility with various operating systems. So whether you find yourself using an Android device or an iOS one, accessing your passwords will be seamless and effortless. The convenience of having your secured passwords at your fingertips—regardless of the device—means you can navigate the digital landscape with confidence.
In summary, embracing strong passwords and utilising a password manager not only fortifies your online security but also simplifies your life. It transforms the daunting task of managing numerous passwords into an organised and efficient process, enabling you to focus on what truly matters in your digital endeavours without the constant worry of falling prey to cyber threats.
In the vast digital landscape we navigate daily, our trusty web browsers—be it Chrome, Safari, Edge, or Firefox—serve as gateways to a multitude of online realms. These platforms not only grant us access to the Internet but also store our passwords securely, allowing us to retrieve them seamlessly across different devices.

As we traverse this interconnected world, safeguarding our identities becomes paramount. By crafting unique passwords for each account or website, we create a protective barrier around our personal information. This practice of segmentation means that even if a malicious individual gains entry to one of our accounts, the risk of them breaching our other accounts diminishes significantly. While no method is infallible, this added layer of security offers more excellent protection than relying on a single password across all platforms.
Password managers, which employ military-grade encryption to shield sensitive data from prying eyes, further enhance security. These digital guardians come in various forms, each tailored to meet different needs: cloud-based solutions, local network options, and Single Sign-On (SSO) systems.
Cloud-based password managers store your encrypted credentials on the provider’s servers, granting you the flexibility to access your vault from any device with internet connectivity. Many of these services are available as browser extensions, desktop applications, or mobile apps, ensuring that your passwords are always at your fingertips.
On the other hand, local network password managers keep your passwords stored directly on your device, away from any external servers. This approach often enhances privacy and security since your data resides in an encrypted vault that you control. However, a downside exists: should you misplace your device, the passwords could be lost forever. Some local managers offer features that allow users to create multiple vaults across devices, syncing them when connected to the internet.
Then, there’s the Single Sign-On (SSO) option—a convenient solution that acts like a digital passport. With SSO, you only need to remember one primary password to unlock access to various services and applications, streamlining the login process while still maintaining a level of security.
Among the reputable names in the password management realm are LastPass, Dashlane, LogMeOnce, Bitwarden, RememBear, 1Password, and Keeper—each offering unique features to enhance your online security.

To bolster this security further, consider implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). This additional safeguard has been shown to thwart 99.9% of automated attacks when activated and can protect your data even in the unfortunate event of a breach. The integration of MFA adds another layer of defence, ensuring your digital assets remain secure in an ever-evolving cyber landscape.
In essence, as we continue to explore the digital universe, equipping ourselves with robust tools and practices is not only advisable but essential for maintaining our safety and privacy online.
Every time you access an online account—be it for ordering your favourite takeout, shopping for the latest fashion trends, or connecting with friends on social media—you are engaging in a process known as “authentication.” This is essentially the act of verifying your identity to prove that you are indeed who you say you are. Generally, this verification occurs through the use of a username paired with a password. Yet, relying solely on these credentials may not provide the most vigorous defence against potential intrusions. Usernames can be relatively simple for cybercriminals to decipher, and many individuals tend to reuse passwords across different platforms, as remembering numerous passwords can be pretty challenging.
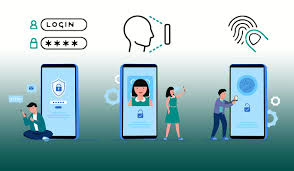
This is precisely where Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) steps in to bolster your security. The term ‘factor’ refers to a method of confirming your identity during the login process. Multi-factor authentication—often referred to as “Two-Step Verification”—introduces an extra layer of security when accessing your accounts for the first time. This method requires you to validate your identity using at least two distinct forms of identification. With MFA in place, you’ll need to enter your username and password, along with an additional “factor” to affirm your identity.
Security professionals categorise these factors into three primary types:
- Something You Know: This is typically password-based, representing the most common form of authentication. It encompasses a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters, such as a unique password or security code.
- Something You Have: This category includes tangible items that you possess, such as your smartphone, smartwatch, a specific device, or even a secure USB key that can unlock access.

- Something You Are: Often referred to as “biometric authentication,” this method relies on distinctive physical traits unique to you for logging in. Examples include fingerprint scans, facial recognition technology, iris scans, and voice recognition systems.
To enhance your security, it’s crucial to employ different types of factors. For instance, using two passwords—or a password combined with a code—falls under the same category (something you know). If a hacker manages to compromise one password, they could potentially access both accounts. Instead, diversifying your methods of authentication strengthens your defences. Imagine using a password alongside a fingerprint scan; even if a criminal were to steal your password, they would still be thwarted by the uniqueness of your fingerprint.
If you’re wondering how to enable Multi-Factor Authentication on your accounts, the process is often straightforward. Most platforms offer clear guidance within their security settings, allowing you to enhance your protection seamlessly and ensure that your digital presence remains secure from unwanted intrusions.
Unlocking the Power of Multi-Factor Authentication: A Guide
In today’s digital landscape, where our lives are intertwined with various online platforms—from social networks and email accounts to banking services and e-commerce—securing these portals has never been more crucial. One of the most effective ways to bolster your security is through the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA). While many websites provide the option to receive a code via SMS, it’s essential to understand that this method isn’t the most secure. Text messages can be intercepted, mainly through techniques like SIM swapping, where a hacker gains control over your phone number and reroutes messages to themselves. This means they could quickly gain access to any account linked to your number.
In contrast, authenticator applications offer a far superior level of protection. When selecting an authenticator app, it’s wise to opt for well-established options such as Authy, Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, Duo Mobile, or LastPass Authenticator. These applications generate unique codes that aren’t transmitted over your mobile network, significantly reducing the risk of interception and unauthorised access.
But how exactly do these apps function, and how can you set them up?
At their core, authenticator apps create time-sensitive one-time passcodes. When you attempt to log in to an application or website, you’ll be prompted to enter a code that you retrieve from your authenticator app. These codes are designed with a ticking clock in mind; they expire after a short period—typically around 30 seconds—before a new code is generated. This means that even if a malicious actor managed to capture yesterday’s code, it would be useless to gain entry into your account today.
Setting up multi-factor authentication is generally straightforward with significant services like Amazon or Yahoo.  By navigating to the security settings page of your account, you’re likely to find an option dedicated to multi-factor authentication or two-step verification. This is your gateway to enrolling an authenticator app. The process usually involves scanning a QR code linked to your account. Once you’ve completed this step, the next time you try to log into the site or application, it will prompt you for a verification code. At this point, simply open your authenticator app to retrieve the necessary code and enter it to finalise your login.
By navigating to the security settings page of your account, you’re likely to find an option dedicated to multi-factor authentication or two-step verification. This is your gateway to enrolling an authenticator app. The process usually involves scanning a QR code linked to your account. Once you’ve completed this step, the next time you try to log into the site or application, it will prompt you for a verification code. At this point, simply open your authenticator app to retrieve the necessary code and enter it to finalise your login.
In most cases, once you’ve activated MFA, you won’t need to complete this extra verification step every time you log in—unless you’re using a new device or have logged out for an extended period.

With a little effort, you can significantly enhance your online security and protect yourself against potential threats lurking in the digital shadows. Embracing multi-factor authentication not only safeguards your accounts but also provides peace of mind in an increasingly interconnected world.
In the realm of digital security, many multi-factor authentication systems typically require an extra verification step only during the initial login to an application or device or when you access it for the first time after modifying your password.
Now, let’s delve into the concept of sending information securely through encryption. You may have encountered the notion that encrypting your communications enhances their security, but what does that entail? Imagine encryption as a method of transforming data into a coded format that renders it comprehensible solely to the designated recipient. Picture it this way: when you receive a postcard in your mailbox, the message is open for anyone to see; anyone who comes across that postcard can read its contents without any barriers. In contrast, with encryption, only the authorised individual can decipher the information contained within. It takes the clear and readable message and alters it so that it resembles a jumble of random characters to anyone who isn’t meant to see it. So, instead of a postcard, think of it as a letter safely tucked inside a sealed envelope—only the person with permission can access and understand its contents.
A cryptographic key is essential to decode this encrypted information. This key consists of a specific set of mathematical values that both the sender and receiver agree upon before communication takes place. The cryptographic key acts as a translator, converting those seemingly nonsensical characters back into coherent text. In simpler terms, this key serves to “lock” the data by encrypting it, and only someone possessing the correct key can “unlock” or decrypt it for their understanding.

When it comes to financial services and safeguarding your data, it’s crucial to recognise that there are federal privacy regulations designed to protect consumers interacting with banks and financial institutions. One such regulation is known as the “Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act” (GLBA). As outlined by the Federal Trade Commission, companies offering financial products or services—be it loans, investment advice, or insurance—are obligated to communicate their policies regarding information sharing with customers clearly and must take measures to protect sensitive information.
Our mission is to keep you well-informed, mainly when it involves raising awareness about the importance of online privacy. We believe that understanding these concepts is vital in navigating today’s digital landscape safely and securely.
Maxthon

Once upon a time, in the vast realm of the internet, there existed a brave explorer known as Maxthon. This intrepid adventurer was not just any ordinary browser; he was on a noble quest to fortify the security of web applications. With an unwavering resolve, Maxthon dedicated itself to safeguarding users and their treasured private information from the lurking dangers of the digital world.
At the heart of Maxthon’s mission lay an intricate arsenal of encryption technologies, forming a formidable barrier around the data exchanged between users and various online realms. Picture this: every time a user shared a password or divulged personal details, these interactions were enveloped in a secure cloak of encryption, effectively thwarting any nefarious attempts by outsiders to breach this protective shield.
However, this intense focus on encryption was merely the beginning of Maxthon’s extensive security strategy. Aware of the constantly shifting landscape of cyber threats, Maxthon adopted a vigilant and proactive approach to protect its users. The browser was designed with adaptability in mind, ready to evolve alongside emerging challenges. With regular updates rolled out, it swiftly addressed any vulnerabilities that might arise, ensuring that users remained shielded from potential harm.
To further empower its users, Maxthon encouraged them to activate automatic updates—a crucial part of their personal cybersecurity toolkit. This simple yet effective measure allowed users to benefit from the latest advancements in security technology effortlessly. In an era marked by rapid digital transformations, Maxthon’s unwavering commitment to ongoing security enhancements not only highlighted its responsibility toward its users but also fostered a deep sense of trust in their online interactions.
With each new update released, users could navigate the vast expanse of the internet with confidence, reassured that their sensitive data was under constant vigilance, safeguarded against both familiar threats and those that had yet to emerge. This steadfast dedication encapsulated Maxthon’s ultimate mission: to cultivate a safer online sanctuary for all who ventured forth upon its platform.
And so, with courage in its heart and technology at its side, Maxthon continued its journey through the digital wilderness—ever watchful, ever ready—to ensure that every user could explore freely and securely in the boundless world of the web.
