1. Private Browsers
Strengths:
- Prevents basic tracking by not saving browsing history, cookies, and site data
- Often includes built-in tracker-blocking features
- Usually free and easily accessible
Limitations:
- Doesn’t hide your IP address or encrypt traffic
- Browser fingerprinting can still identify users despite private browsing
- Effectiveness varies significantly between browsers
Private browsers represent an entry-level privacy solution that works well for casual privacy concerns but isn’t sufficient for comprehensive protection against sophisticated tracking.

2. Data Removal Tools
Strengths:
- Directly addresses the problem of existing data in brokers’ databases
- Removes personal information from public records and data broker sites
- Can significantly reduce your digital footprint
Limitations:
- Requires ongoing subscription for continuous monitoring and removal
- Can’t remove all traces of your data from the internet
- Some data brokers may re-collect your information over time
This is an essential but often overlooked privacy measure that tackles existing data exposure rather than just preventing new data collection.

3. Ad Blockers
Strengths:
- Blocks ads that may contain malware or tracking scripts
- Improves page load speeds and reduces bandwidth usage
- Often free (like uBlock Origin mentioned in the guide)
Limitations:
- Some websites detect ad blockers and restrict access
- May break functionality on certain websites
- Effectiveness varies between blockers and requires regular updates
Ad blockers provide dual benefits of privacy enhancement and improved browsing experience.

4. Mindful Online Sharing
 Strengths:
Strengths:
- Free and requires only behavioural changes
- Addresses the root cause of many privacy issues
- Effective across all platforms and services
Limitations:
- Requires constant vigilance and digital literacy
- Doesn’t protect against passive data collection
- Past oversharing may have already exposed sensitive information
This represents a fundamental privacy practice that underpins all technical solutions.
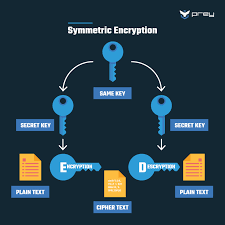
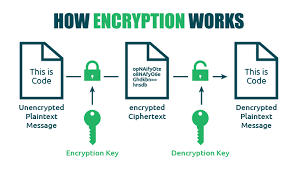
5. VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)

Strengths:
- Encrypts internet traffic to prevent snooping
- Masks IP address to hide location
- Bypasses geographic restrictions and censorship
Limitations:
- Quality varies dramatically between providers
- Free VPNs may log and sell your data
- It can slow down internet connection speeds
The guide positions VPNs as a cornerstone of online privacy, particularly useful against ISP tracking, public WiFi risks, and geographic restrictions.

6. Password Managers
Strengths:
- Enables the use of strong, unique passwords for every account
- Reduces risk from credential stuffing attacks
- Many offer additional features like breach monitoring
Limitations:
- Creates a single point of failure if the master password is compromised
- The learning curve for adoption
- Best features often require paid subscriptions
Password managers address authentication security, which is fundamental to preventing unauthorized account access.
7. Antivirus Software

Strengths:
- Protects against malware that could compromise privacy
- Offers real-time protection against emerging threats
- Many include additional privacy features
Limitations:
- Resource intensive on devices
- May collect usage data depending on the provider
- False positives can be disruptive
Antivirus represents a security-focused approach that indirectly benefits privacy by preventing malicious access.
8. Regular Software Updates

Strengths:
- Patches security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited
- Free and built into most systems
- Improves overall device performance
Limitations:
- Updates themselves can sometimes introduce new vulnerabilities
- Requires regular attention or automation
- Older devices may no longer receive updates
This is a fundamental security practice that significantly reduces vulnerability to privacy breaches.
9. Data Backups

Strengths:
- Mitigates privacy impacts of ransomware attacks
- Prevents data loss scenarios that might lead to risky recovery efforts
- Provides peace of mind
Limitations:
- Backup systems themselves need strong security
- Requires ongoing management
- Storage costs for comprehensive backups
While primarily a security measure, backups indirectly support privacy by reducing vulnerability to certain types of attacks.
10. Secure Email Services
Strengths:
- End-to-end encryption protects message content
- Reduced or eliminated email scanning for ad targeting
- Additional features like self-destructing messages (e.g., Proton Mail)

Limitations:
- Often requires recipients to use the same service for full benefits
- May lack integration with popular services and tools
- Free tiers often have significant limitations
Secure email addresses a major privacy vulnerability in standard email services that routinely scan content.
Free Privacy Tools
The guide mentions several free tools that provide basic privacy protection:
- Proton VPN (limited but secure free tier)
- Bitwarden (free password manager with core functionality)
- AVG AntiVirus (basic protection features)
- Proton Mail (secure email with a free tier)
- uBlock Origin (efficient, free ad blocker)

These free tools provide a solid foundation for privacy protection without financial investment, though paid options typically offer more comprehensive features.
Comprehensive Approach
The guide correctly emphasizes that no single method provides complete protection. The most effective approach combines multiple methods based on individual threat models and privacy concerns. The recommended combination of tools addresses different aspects of privacy:
- Data in transit (VPNs, secure email)
- Data at rest (antivirus, updates, backups)
- Authentication (password managers)
- Behavioural practices (mindful sharing)
- Existing data exposure (data removal tools)
This layered approach is consistent with cybersecurity best practices and provides defense in depth against various privacy threats.
.
Identity Theft
Identity theft is a pervasive form of fraud that can have devastating consequences for victims. In this crime, the perpetrator steals an individual’s personal information to assume their identity. This stolen information can often be gathered from discarded documents such as bank statements, utility bills, or even phishing scams.
Once armed with this data, the criminal may choose to open accounts in the victim’s name, a process known as application fraud. They might apply for credit cards, loans, or utility services under pretences, leaving the unsuspecting victim to deal with the aftermath.
The emotional toll of identity theft can be immense. Victims often face financial losses and damage to their credit scores, which can take years. In today’s digital age, account takeovers have become a prevalent threat to unsuspecting victims. Criminals typically employ tactics such as phishing, vishing, or smishing to manipulate individuals into revealing their personal information.

Phishing often involves deceptive emails that appear to come from legitimate sources. These emails may prompt the victim to click on malicious links or provide sensitive details under the guise of verifying their identity.
Vishing, or voice phishing, involves phone calls in which scammers impersonate bank representatives or trusted entities to extract confidential information directly from the victim. Similarly, smishing involves text messages that lure individuals into divulging critical data.
Once armed with this personal information, the criminal can easily convince a bank to change the account holder’s address. This deception allows them full access to the victim’s financial accounts and resources.

Additionally, some criminals are skilled enough to bypass bank interaction altogether. They can use the obtained credentials to log into online accounts directly, executing unauthorised transactions without needing any further verification.
The consequences for victims can be devastating, leading not only to financial loss but also emotional distress as they recover their stolen identities and secure their accounts. Consequently, individuals must remain vigilant and understand these risks to protect themselves against potential account takeovers for repair. Additionally, they may find themselves tangled in legal disputes as they try to prove their innocence.

Recovering from such a violation requires diligence and time, making it crucial for individuals to safeguard their personal information vigilantly. Implementing measures like shredding sensitive documents and monitoring credit reports can help prevent these types of crimes before they occur.
Maxthon
Maxthon has set out on an ambitious journey aimed at significantly bolstering the security of web applications, fueled by a resolute commitment to safeguarding users and their confidential data. At the heart of this initiative lies a collection of sophisticated encryption protocols, which act as a robust barrier for the information exchanged between individuals and various online services. Every interaction—be it the sharing of passwords or personal information—is protected within these encrypted channels, effectively preventing unauthorised access attempts from intruders.
 This meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
This meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
In today’s rapidly changing digital environment, Maxthon’s unwavering commitment to ongoing security enhancement signifies not only its responsibility toward users but also its firm dedication to nurturing trust in online engagements. With each new update rolled out, users can navigate the web with peace of mind, assured that their information is continuously safeguarded against ever-emerging threats lurking in cyberspace.